Section 10 Direct Memory Access Controller
R01UH0134EJ0400 Rev. 4.00 Page 421 of 2108
Sep 24, 2014
SH7262 Group, SH7264 Group
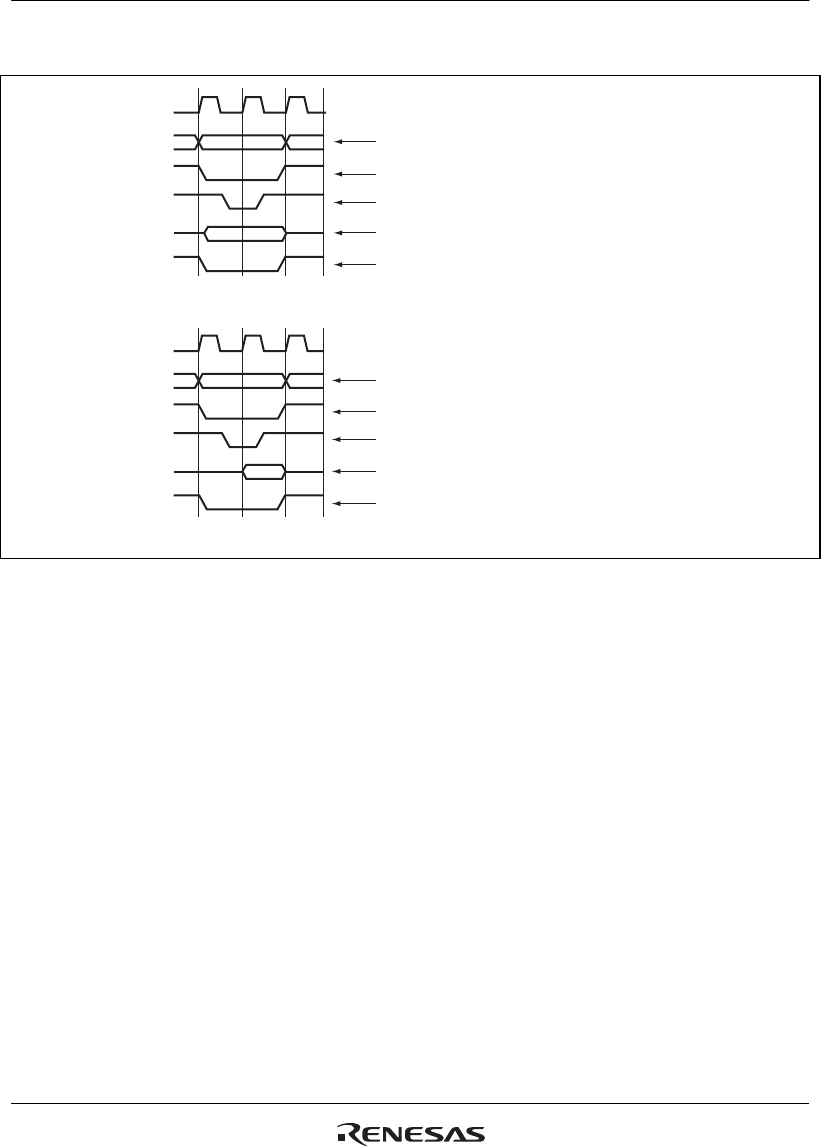
Figure 10.6 shows an example of DMA transfer timing in single address mode.
Address output to external memory space
Select signal to external memory space
Select signal to external memory space
Data output from external device with DACK
DACK signal (active-low) to external device with DACK
Write strobe signal to external memory space
Address output to external memory space
Data output from external memory space
DACK signal (active-low) to external device with DACK
Read strobe signal to external memory space
(a) External device with DACK → External memory space (normal memory)
(b) External memory space (normal memory) → External device with DACK
CK
A25 to A0
D15 to D0
DACKn
CSn
WEn
CK
A25 to A0
D15 to D0
DACKn
CSn
RD
Figure 10.6 Example of DMA Transfer Timing in Single Address Mode
(2) Bus Modes
There are two bus modes; cycle steal and burst. Select the mode by the TB bits in the channel
control registers (CHCR).
(a) Cycle Steal Mode
Normal mode
In normal mode of cycle steal, the bus mastership is given to another bus master after a one-
transfer-unit (byte, word, longword, or 16-byte unit) DMA transfer. When another transfer
request occurs, the bus mastership is obtained from another bus master and a transfer is
performed for one transfer unit. When that transfer ends, the bus mastership is passed to
another bus master. This is repeated until the transfer end conditions are satisfied.
The cycle-steal normal mode can be used for any transfer section; transfer request source,
transfer source, and transfer destination.


















