Section 3 Floating-Point Unit (FPU)
R01UH0134EJ0400 Rev. 4.00 Page 99 of 2108
Sep 24, 2014
SH7262 Group, SH7264 Group
3.2.2 Non-Numbers (NaN)
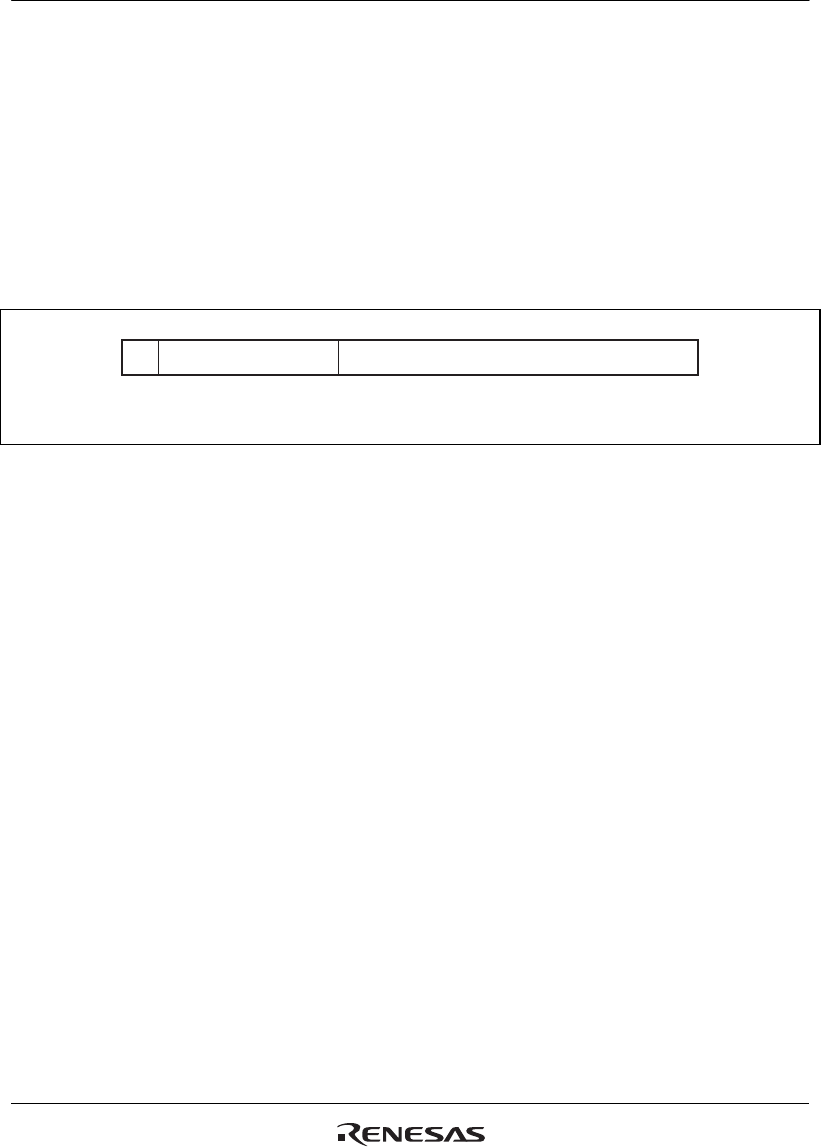
Figure 3.3 shows the bit pattern of a non-number (NaN). A value is NaN in the following case:
Sign bit: Don't care
Exponent field: All bits are 1
Fraction field: At least one bit is 1
The NaN is a signaling NaN (sNaN) if the MSB of the fraction field is 1, and a quiet NaN (qNaN)
if the MSB is 0.
31 30 23 22 0
x
N = 1: sNaN
N = 0: qNaN
11111111
Nxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Figure 3.3 Single-Precision NaN Bit Pattern
An sNaN is input in an operation, except copy, FABS, and FNEG, that generates a floating-point
value.
When the EN.V bit in FPSCR is 0, the operation result (output) is a qNaN.
When the EN.V bit in FPSCR is 1, an invalid operation exception will generate FPU exception
processing. In this case, the contents of the operation destination register are unchanged.
If a qNaN is input in an operation that generates a floating-point value, and an sNaN has not been
input in that operation, the output will always be a qNaN irrespective of the setting of the EN.V bit
in FPSCR. An exception will not be generated in this case.
The qNAN values as operation results are as follows:
Single-precision qNaN: H'7FBF FFFF
Double-precision qNaN: H'7FF7 FFFF FFFF FFFF
See the individual instruction descriptions for details of floating-point operations when a non-
number (NaN) is input.


















