8 - 5
8. CALCULATION METHODS FOR DESIGNING
8.5 Capacity selection
As a first step, confirm the load conditions and temporarily select the servo motor capacity. Then,
determine the operation pattern, calculate required torques according to the following equations, and
check that the servo motor of the initially selected capacity may be used for operation .
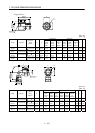
(1) Initial selection of servo motor capacity
After calculating the load torque (T
L) and load inertia moment (JL), select a servo motor which will
satisfy the following two relationships:
Servo motor's rated torque
TL
Servo motor JM JL/m
m
3 : High duty (more than 100 times/min.)
Settling time 40ms or less
m
5 : Middle duty (60 to 100 times/min.)
Settling time 100ms or less
m
permissible load inertia moment : Low duty (less than 60 times/min.)
Settling time more than 100ms
Find the acceleration and deceleration torques and continuous effective load torque as described in (2)
to make a final selection. For high-duty positioning, the load inertia moment (J
L) value should be as
small as possible. If positioning is infrequent as in line control, the load inertia moment (J
L) value may
be slightly larger than in the above conditions.
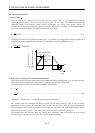
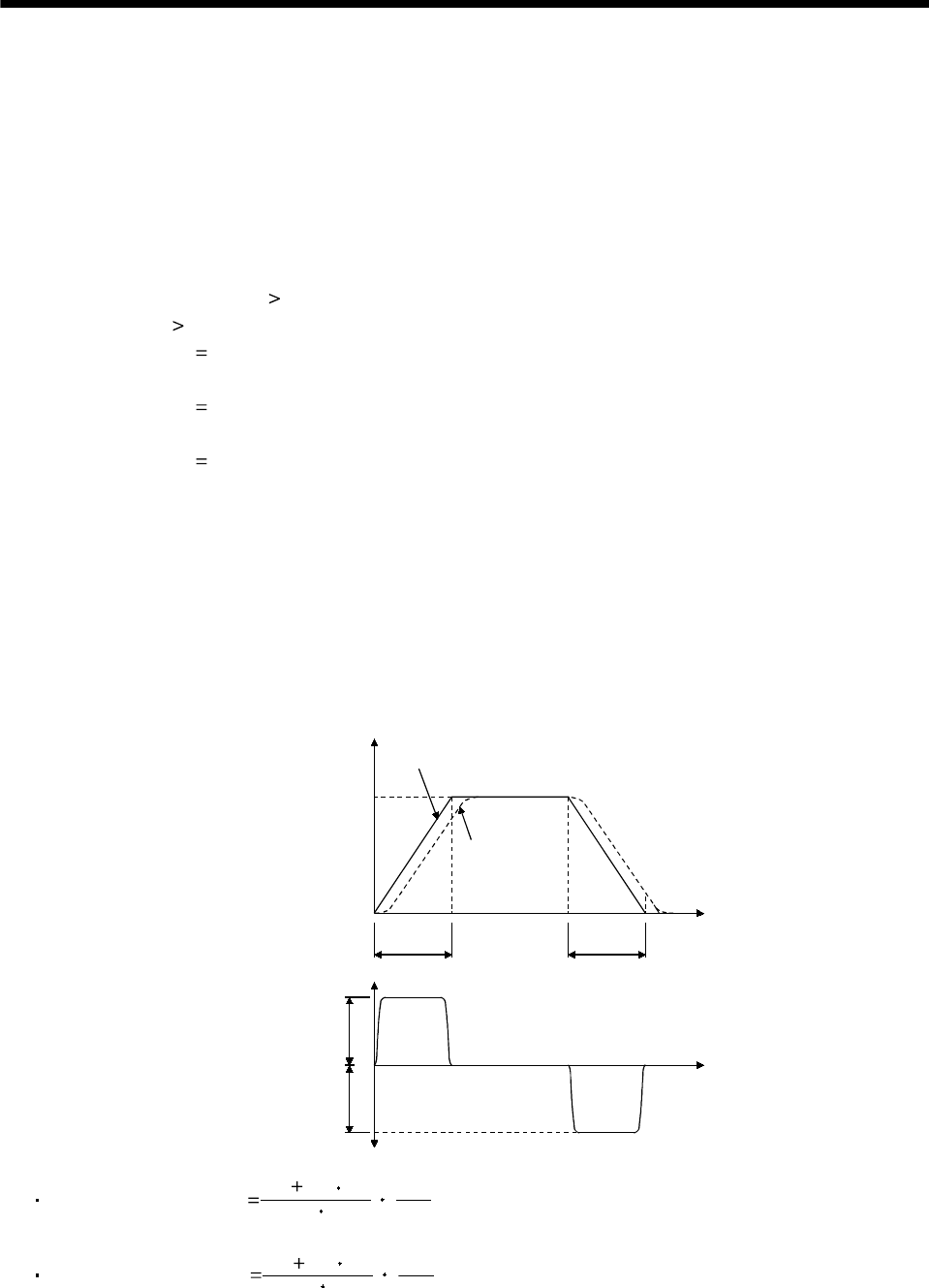
(2) Acceleration and deceleration torques
The following equations are used to calculate the acceleration and deceleration torques in the
following operation pattern:
C
o
m
m
a
n
d
p
u
l
s
e
S
e
r
v
o
m
o
t
o
r
s
p
e
e
d
[
r
/
m
i
n
]
0
0
Nofo
Time
Time
Command
Servo motor
speed
t
psa
T
a
T
d
Deceleration
torque
A
cceleration
torque
f
r
e
q
u
e
n
c
y
f
[
p
p
s
]
t
psd
Acceleration torque Ta
9.55 10
4
(J
L
J
M
) No
tpsa
1
........................................................................................(8.9)
Deceleration torque Td
9.55 10
4
(JL JM) No
tpsd
1
.....................................................................................(8.10)