8 - 4
8. CALCULATION METHODS FOR DESIGNING
8.4 Stopping characteristics
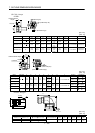
(1) Droop pulses (
)
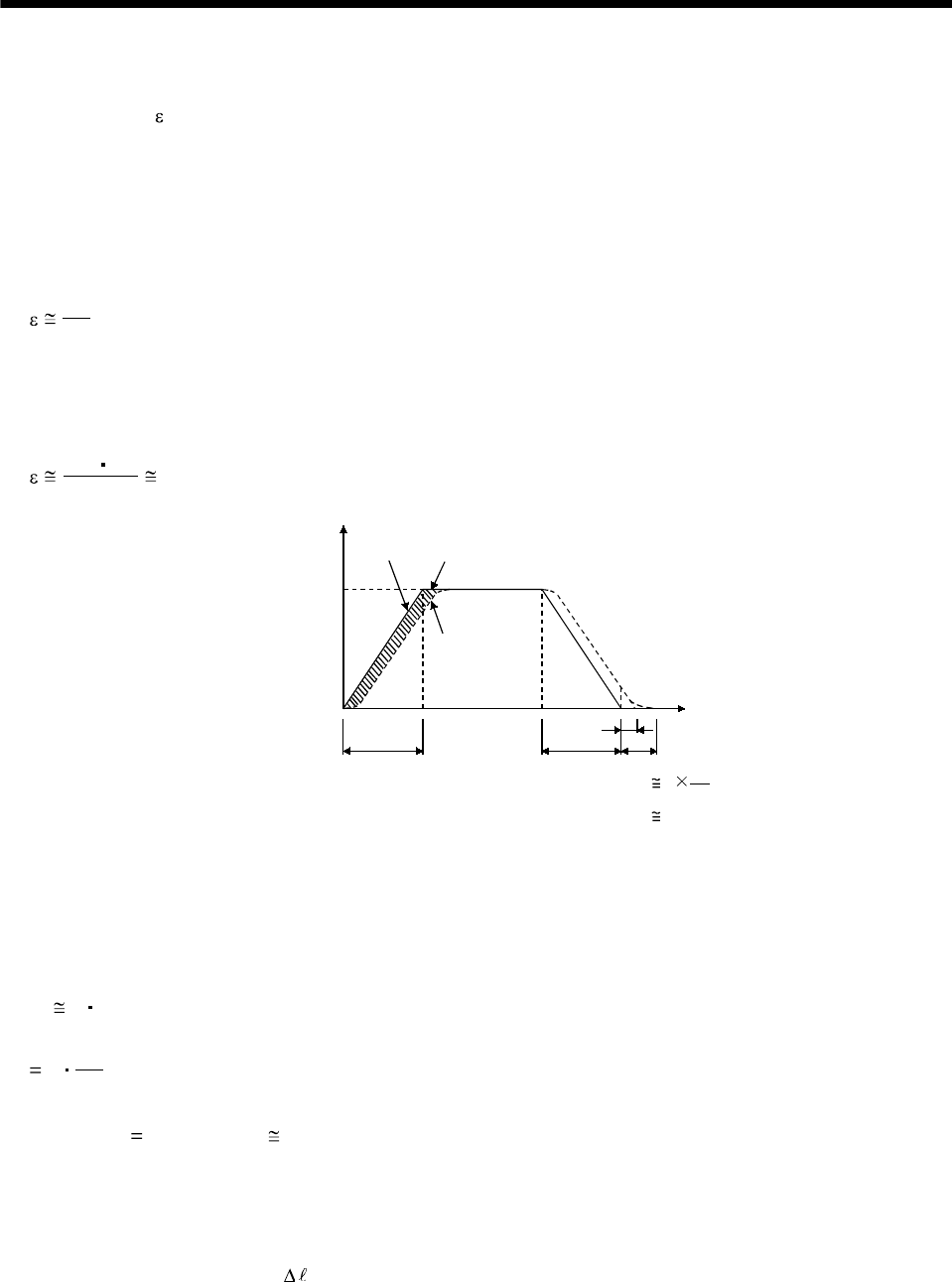
When a pulse train command is used to run the servo motor, there is a relationship between the
command pulse frequency and servo motor speed as shown in the figure. The difference between the
command pulses and feedback pulses during acceleration are called droop pulses, which are
accumulated in the servo amplifier's deviation counter. Equation 8.7 defines a relationship between
the command pulse frequency (f) and position control gain 1(Kp).
f0
Kp
[pulse] ...............................................................................................................................................(8.7)
Supposing that the value of position control gain 1 is 70 [rad/s], the droop pulses during operation will
be as follows at the command pulse frequency of 200 [kpps] according to Equation 15.1:
1
200 10
3
2858[pulse]
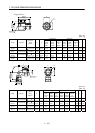
Command pulse frequency f
Servo motor speed
[pps][r/min]
0
Time
Command
Droop pulses
Servo motor
speed
t
psa
t
s
t
s
3
1
70
0.04
T
p
t
psd
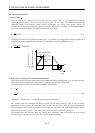
(2) Settling time (ts) during linear acceleration/deceleration
Since droop pulses still exist when there are no command pulses, settling time (ts) is required until the
servo motor stops. Set the operation pattern in consideration for the settling time.
The settling time (ts) value is obtained according to Equation 8.8:
ts
3 Tp
3
1
Kp
[s] ....................................................................................................................................................(8.8)
*When Kp
70 [rad/s], ts 0.04 [s]. (Refer to the above diagram.)
The settling time (ts) indicates the time required for the servo motor to stop in the necessary
positioning accuracy range. This does not always mean that the servo motor has stopped completely.
Thus, especially when the servo motor is used in high-duty operation and positioning accuracy has no
margin for travel per pulse (
), the value obtained by Equation 8.8 must be increased.
The settling time (ts) will vary with the moving part conditions. Especially when the load friction
torque is large, movement may be unstable near the stopping position.