6 - 121
6 POSITIONING CONTROL
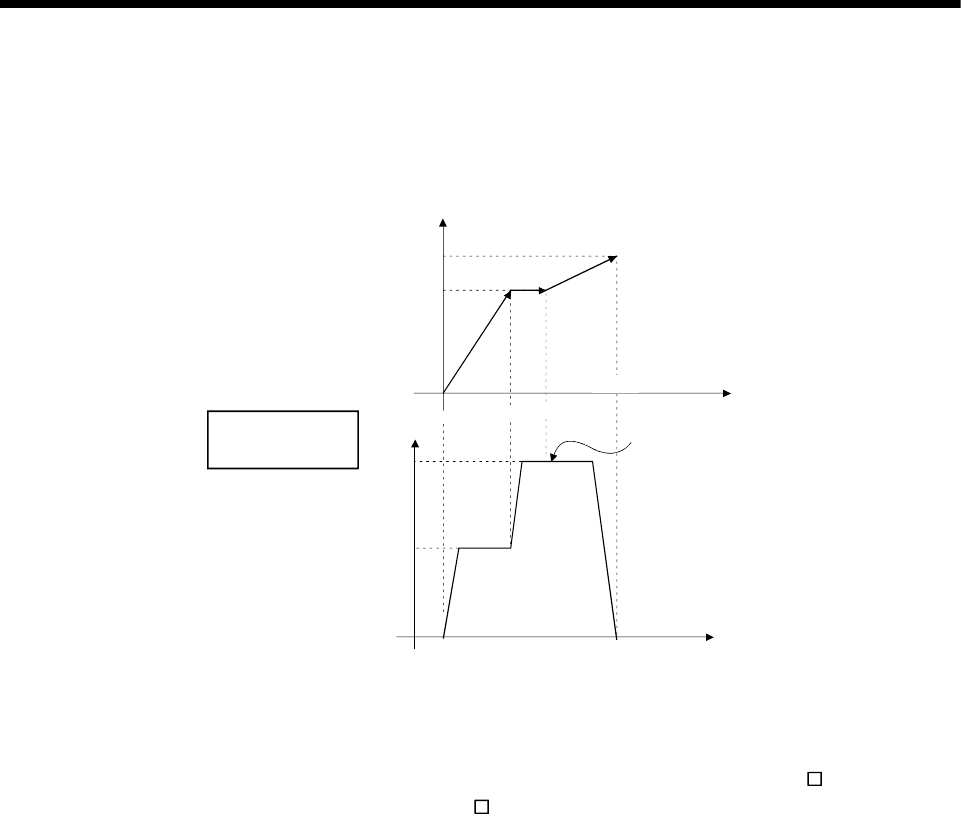
[Operation timing]
Operation timing for constant-speed control is shown below.
[Example : Operation timing for 2 axes constant-speed control]
Change speed after speed-switching
Axis 3 positioning direction
P1
80000
60000
Axis2 positioning direction
P2
P3
15000
Positioning speed
for 2 axes linear
interpolation
V
10000
t
Set
speed
40000
60000
100000
0
0
[Caution]
(1) The number of control axes cannot be changed during control.
(2) The pass point can be specified the absolute data method (ABS
) and
incremental method (INC
) by mixed use.
(3) The pass point can also be specified an address which change in travel direction.
The acceleration processing at a pass point is executed for 1 axis constant-speed.
However, the acceleration/deceleration processing at a pass point is not executed
for 2 to 4 axes constant-speed, so be careful of the servo error occurrence, etc.
(4) Speed change is possible after the start.
Note the following points at the speed change.
(a) The central point-specified circular interpolation is included the constant-
speed control.
When the arc path calculated from the start address and central-point
address is differ (within the allowable error range for circular interpolation)
from the setting end address, if the speed is changed, error compensation
(Refer to Section 4.3.3) may not function normally.
When the central point-specified circular interpolation as positioning method
is used at the constant-speed control, set the start address, central point
address and end address becomes arc correctly.