6 - 23
6 POSITIONING CONTROL
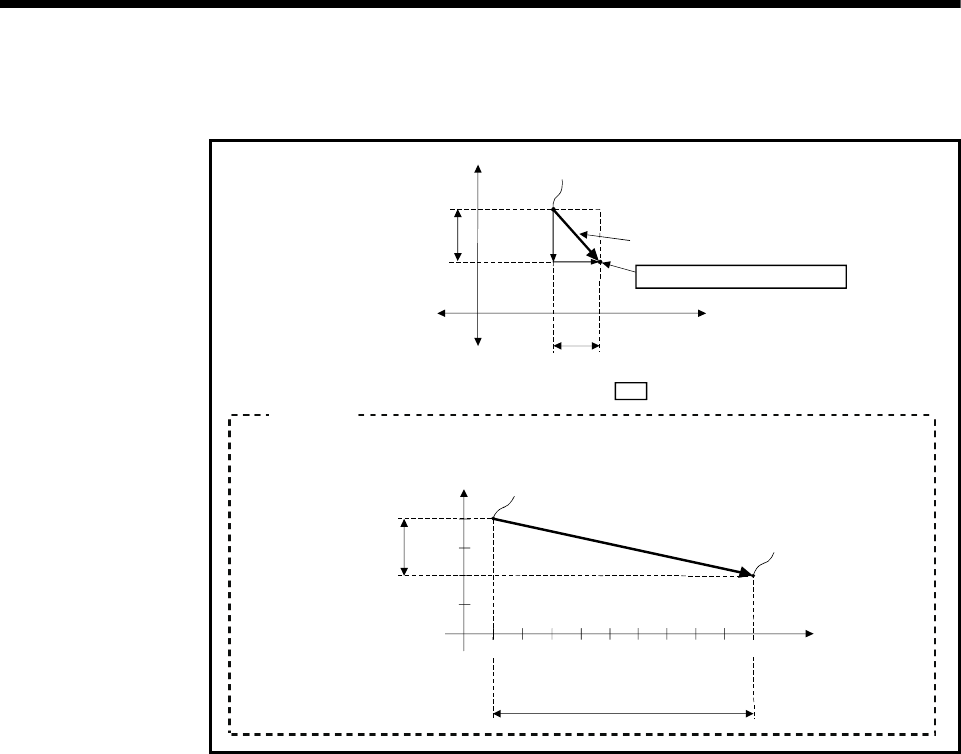
(2) The travel direction is set by the stop address (starting address) and positioning
address of each axis.
Forward
direction
Y
1
Y
2
Y-axis travel value
Reverse
direction
Reverse
direction
Current stop address
(X
1
, Y
1
)
Positioning address (X
2
,
Y
2
)
Operation for X-axis, Y-axis
linear interpolation
X-axis travel value
X
1
X
2
: Indicates setting data
Forward direction
0
(Note)
When the current stop address is (1000, 4000), and the positioning address
is (10000, 2000).
Current stop address
Positioning address
Y-axis travel value
(4000 - 2000 = 2000)
X-axis travel value
(10000 - 1000 = 9000)
4000
2000
05000
10000
1000
Fig.6.3 Positioning using absolute data method
Example