6 - 8
6 POSITIONING CONTROL
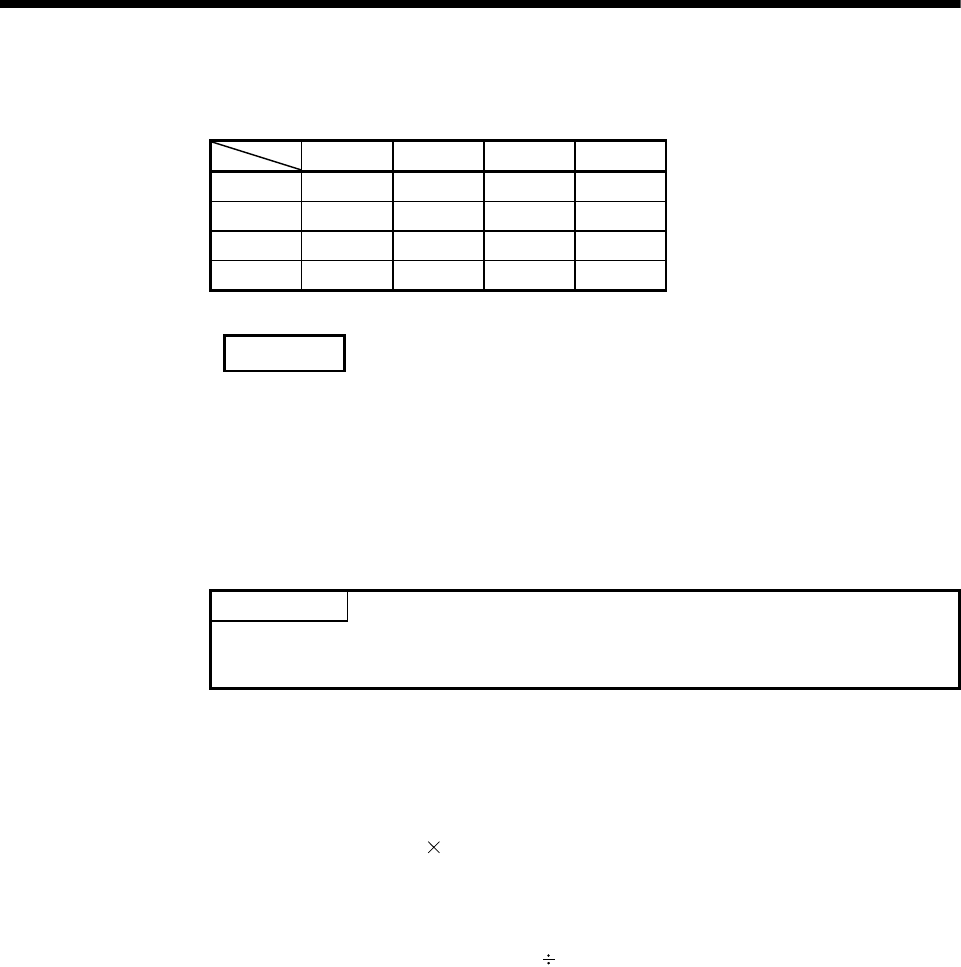
(2) The combinations of each axis control units for interpolation control are shown in
the table below.
Mm inch degree PLS
mm 1) 2) 3) 3)
inch 2) 1) 3) 3)
degree 3) 3) 1) 3)
PLS 3) 3) 3) 1)
Remarks
1): Same units
2): Combination of [mm] and [inch]
3): Unit mismatch
(a) Same units ( 1) )
The position command is calculated with the setting address (travel value),
positioning speed or electronic gear, the positioning is executed.
POINT
If control units for one axis are "degrees" at the circular interpolation control, use
"degrees" also for the other axis.
(b) Combination of [mm] and [inch] ( 2) )
• If interpolation control units are [mm], positioning is controlled by calculating
position commands from the address, travel value, positioning speed and
electronic gear, which have been converted to [mm] using the formula: inch
setting value
25.4 = mm setting value.
• If interpolation control units are [inch], positioning is controlled by
calculating position commands from the address, travel value, positioning
speed and electronic gear, which have been converted to [inch] using the
formula: mm setting value
25.4 = inch setting value.
(c) Discrepancy units ( 3) )
• The travel value and positioning speed are calculated for each axis.
a) The electronic gear converts the travel value for the axis to [PLS].
b) For axis where the units match, the electronic gear converts the
positioning speed to units of [PLS/s].
Positioning is conducted using position commands calculated from
travel values converted to [PLS] and speeds and electronic gear
converted to [PLS/s].
• If the interpolation control units match for two or more axes at the 3-axes or
more linear interpolation, the positioning speed is calculated with the
electronic gear for the axis with the lowest No.


















