Section 33 Power-Down Modes
R01UH0134EJ0400 Rev. 4.00 Page 1813 of 2108
Sep 24, 2014
SH7262 Group, SH7264 Group
(2) Canceling Deep Standby Mode
Deep standby mode is canceled by interrupts (NMI or realtime clock alarm interrupt), change on
the pins for canceling, or a reset (power-on reset). The realtime clock alarm interrupt can always
cancel deep standby mode regardless of the interrupt priority level or the status register (SR)
setting in the CPU. When canceling the mode by a source other than a reset, a power-on reset
exception handling is executed instead of an interrupt exception handling.
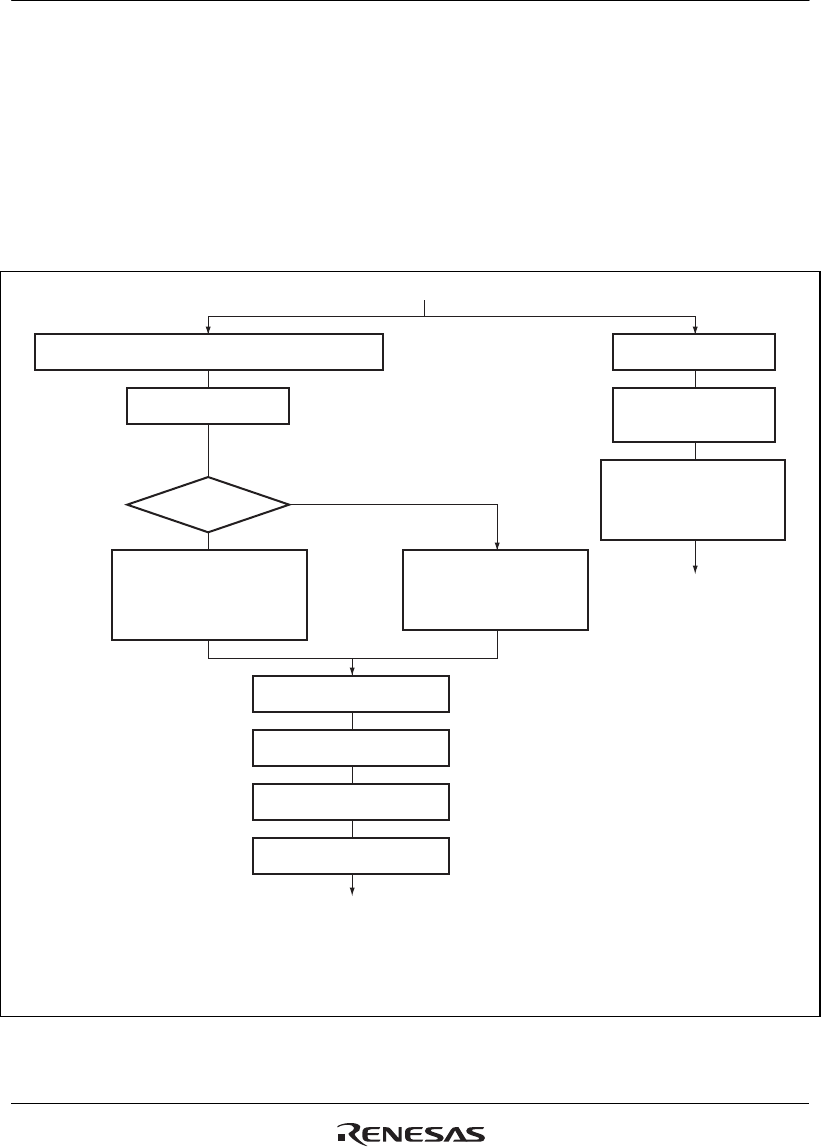
Figure 33.3 shows the flowchart of canceling deep standby mode.
Detect an interrupt (NMI or realtime clock alarm).
Detect change on the pins for canceling.
Count oscillation settling
time
No
Ye s
Detect RES
The RES pin is held low
during oscillation settling
time
Power-on reset
exception handling
according to the boot mode
specified for the reset
To the initialization routine
Power-on reset exception handling
[1-Mbyte version]
Read PC from H'FFFF8000
Read SP from H'FFFF8004
[640-Kbyte version]
Read PC from H'1C000000
Read SP from H'1C000004
Power-on reset
exception handling
according to the boot mode
specified for the reset
Check the flags in DSFR
Processing according to deep
standby mode cancel source
Reconfiguration of
peripheral functions*
Clear the IOKEEP bit in DSFR
(Release the pin state retention)
To the state before the transition
to deep standby mode
Deep standby mode
RAMBOOT=1?
Note: * Peripheral functions include all functions such as the clock pulse generator, interrupt controller,
bus state controller, general I/O ports, and peripheral modules.
Figure 33.3 Flowchart of Canceling Deep Standby Mode