ARCHITECTURE
AND
INSTRUCTIONS
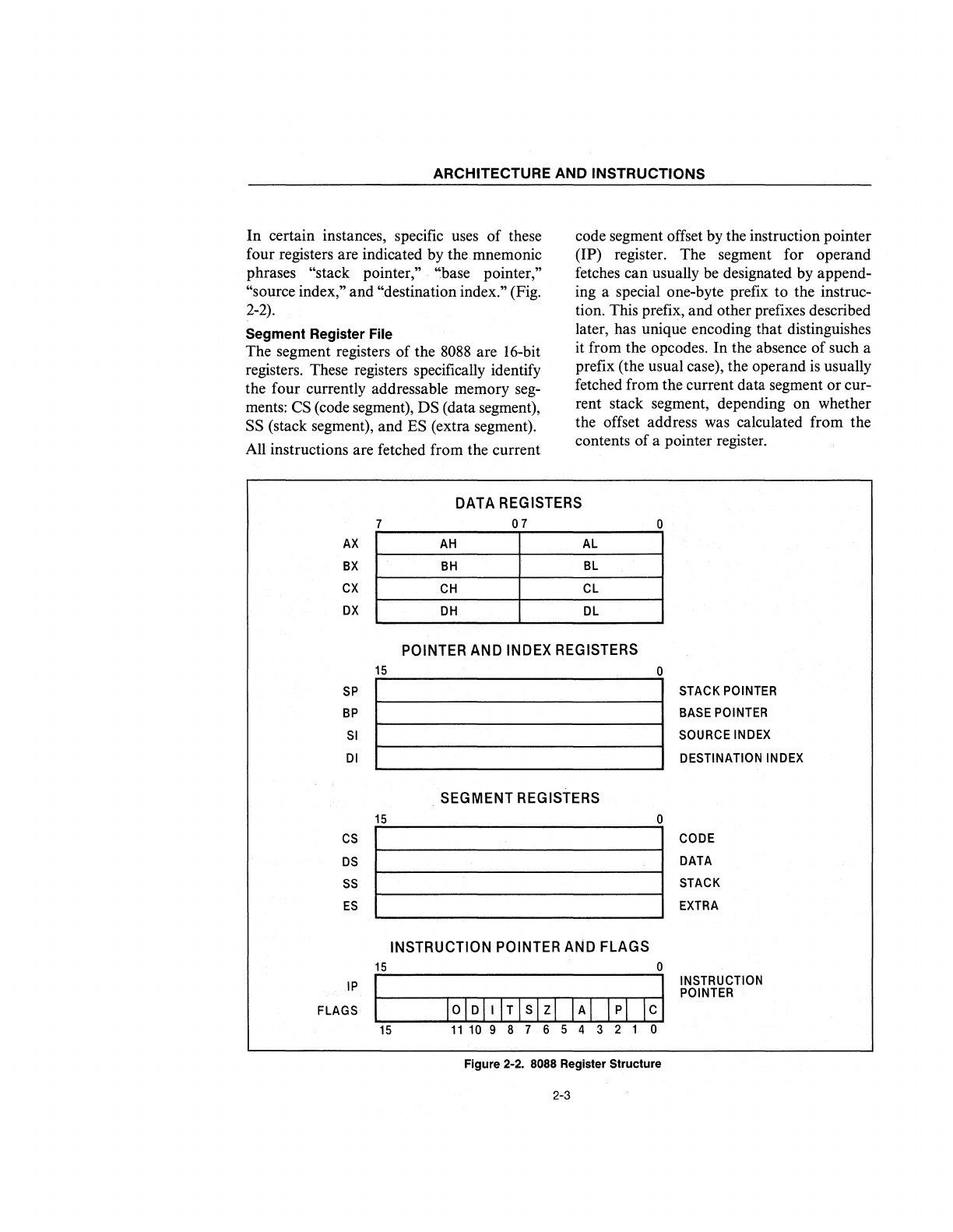
In certain instances, specific uses of these
four registers are indicated by the mnemonic
phrases
"stack pointer," "base pointer,"
"source index,"
and "destination index." (Fig.
2-2).
Segment Register File
The segment registers of the
8088
are 16-bit
registers. These registers specifically identify
the four currently addressable memory seg-
ments:
CS (code segment), DS (data segment),
SS (stack segment), and ES (extra segment).
All instructions are fetched from the current
code segment offset by the instruction pointer
(IP) register. The segment for operand
fetches can usually be designated by append-
ing a special one-byte prefix to the instruc-
tion. This prefix, and other prefixes described
later, has unique encoding that distinguishes
it from the opcodes. In the absence of such a
prefix (the usual case), the operand
is
usually
fetched from the current data segment or cur-
rent stack segment, depending on whether
the offset address was calculated from the
contents of a pointer register.
7
DATA
REGISTERS
07
o
AX
BX
CX
OX
SP
BP
SI
DI
CS
OS
SS
ES
IP
FLAGS
AH
AL
BH
BL
CH
CL
DH
DL
POINTER
AND
INDEX
REGISTERS
15
0
I
I
SEGMENT
REGISTERS
15
0
I I
INSTRUCTION
POINTER
AND
FLAGS
15
0
I
lolDlllTlslzl
IA
I
I
pi
lei
15
11
10
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Figure 2-2.
8088
Register Structure
2-3
STACK
POINTER
BASE
POINTER
SOURCE
INDEX
DESTINATION
INDEX
CODE
DATA
STACK
EXTRA
INSTRUCTION
POINTER


















