INTRODUCTION
To,(ITovide extra drive capability for the data
. ·-lines, the 8286 and
8287
8-bit transceivers are
available; the
8287
being the inverting version
of
the
8286.
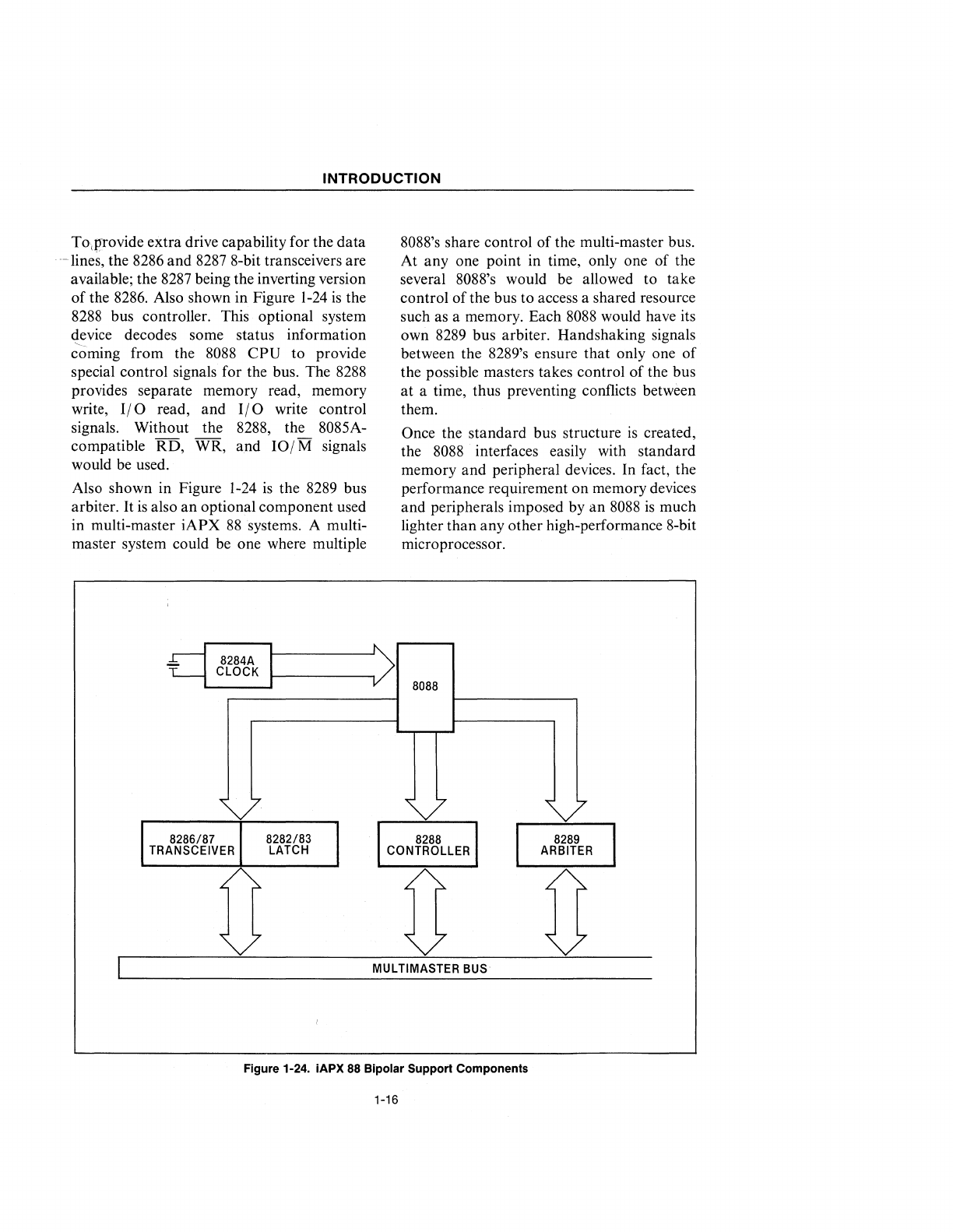
Also shown in Figure
1-24
is
the
8288
bus controller. This optional system
device decodes some status information
~ming
from the
8088
CPU to provide
special control signals for the bus. The
8288
provides separate memory read, memory
write,
110 read, and 110 write control
signals. Without the 8288, the
8085A-
compatible RD, WR, and
101
M signals
would
be
used.
Also shown in Figure
1-24
is
the 8289 bus
arbiter.
It
is
also an optional component used
in multi-master
iAPX
88
systems. A multi-
master system could be one where multiple
q
I
8284A
CLOCK
~7
8286/87
8282/83
TRANSCEIVER
LATCH
/\,.
V
>
8088's share control of the multi-master bus .
At
anyone
point in time, only one of the
several 8088's would
be
allowed to take
control of the bus to access a shared resource
such as a memory. Each
8088
would have its
own
8289
bus arbiter. Handshaking signals
between the 8289's ensure that only one
of
the possible masters takes control
of
the bus
at a time, thus preventing conflicts between
them.
Once the standard bus structure
is
created,
the
8088
interfaces easily with standard
memory and peripheral devices. In fact, the
performance requirement on memory devices
and peripherals imposed by an
8088
is
much
lighter than any other high-performance 8-bit
microprocessor.
8088
V
V
8288 8289
CONTROLLER
I
ARBITER
I
D D
MULTIMASTER
BUS
Figure 1-24. iAPX
88
Bipolar Support Components
1-16