INTRODUCTION
8088
instruction stream. The instructions that
the
NPX interprets as special purpose numer-
ics instructions are regarded almost like
"no-operations" for the
8088.
The NPX con-
tains an additional register set of eight
80-bit
floating point registers which are mani-
pulated with by the additional numerics
instructions. Together, the
8088
with the
NPX have approximately
100
times the per-
formance of a standalone
iAPX
88
system
for numerics-intensive applications.
I/O
Processor
The
8089
lOp, on the other hand, does not
receive instructions from the
8088
instruction
stream.
It
is
a separate microprocessor with its
own instruction set. The
lOP
is
an input/output
channel processor and off-loads
110
interfac-
ing
from the
8088
general purpose CPU. The
lOP's instruction set, different from the
8088,
is specifically tailored for peripheral control
and high speed data transfer. With the
lOp, it
is
I
8088
CPU
8087
NPX
SYSTEM
BUS
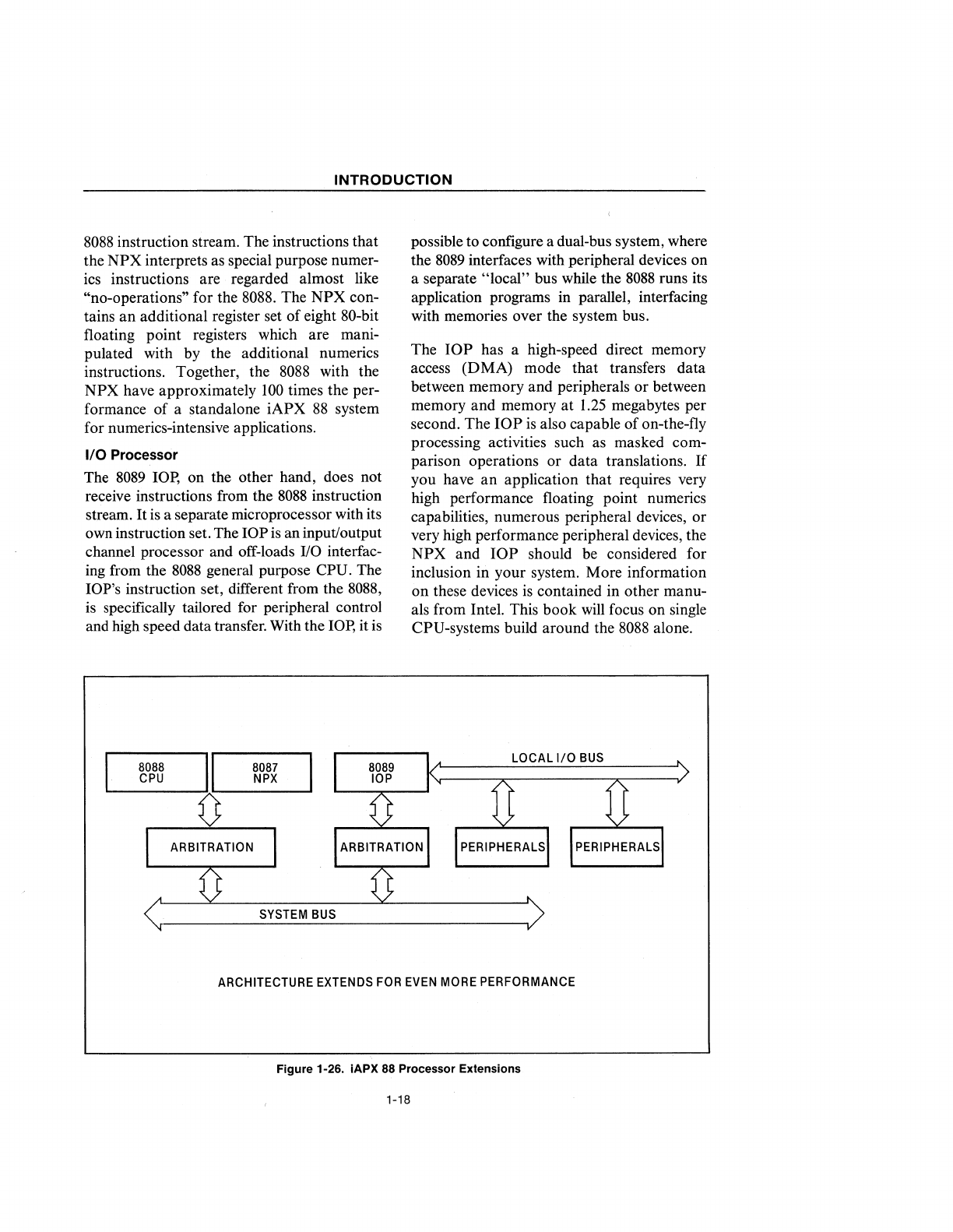
possible to configure a dual-bus system, where
the
8089
interfaces with peripheral devices on
a separate
"local" bus while the
8088
runs its
application programs in parallel, interfacing
with memories over the system bus.
The
lOP
has a high-speed direct memory
access (DMA) mode that transfers data
between memory and peripherals or between
memory and memory at
1.25
megabytes per
second. The
lOP
is
also capable of on-the-fly
processing activities such as masked com-
parison operations or data translations.
If
you have
an
application that requires very
high performance floating point numerics
capabilities, numerous peripheral devices, or
very high performance peripheral devices, the
NPX and
lOP
should be considered for
inclusion in your system. More information
on these devices
is
contained in other manu-
als from Intel. This book
will
focus on single
CPU-systems build around the
8088
alone.
LOCAL
1/0
BUS
ARCHITECTURE
EXTENDS
FOR
EVEN
MORE
PERFORMANCE
Figure 1-26. iAPX
88
Processor Extensions
1-18