Theory of Operation T400 Ozone Analyzer Operator’s Manual
280
13.2. PNEUMATIC OPERATION
Note It is important that the sample airflow system is both leak tight and not
pressurized over ambient pressure. Regular leak checks should be
performed on the analyzer as described in the maintenance schedule,
Table 11-1. Procedures for correctly performing leak checks can be
found in Section 11.3.4.
13.2.1. SAMPLE GAS AIR FLOW
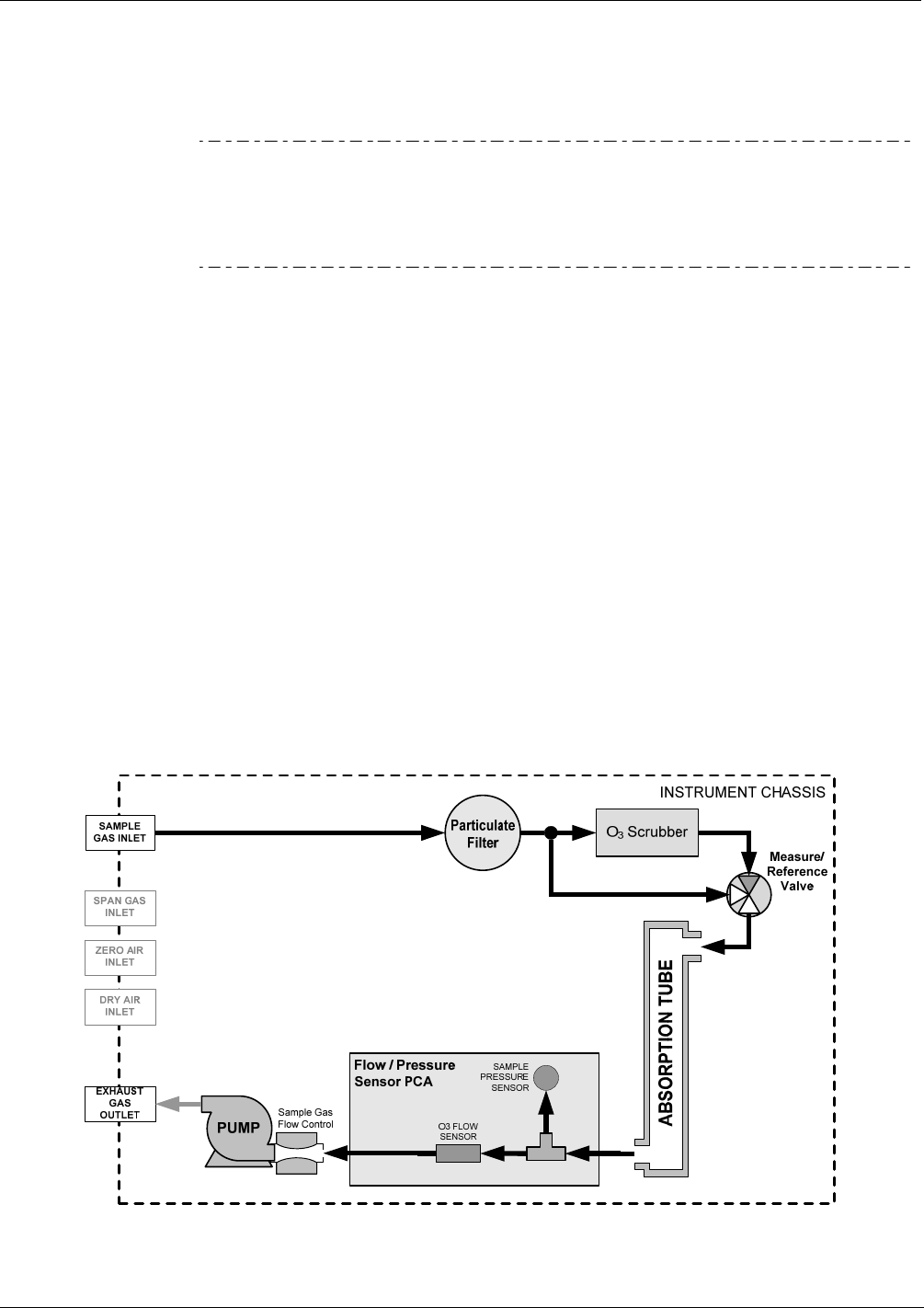
The flow of sample gas through the T400 analyzer is produced by an internal pump that
draws a small vacuum on the downstream side of a critical flow orifice thereby creating
a controlled airflow through the analyzers absorption tube and other components. This
requires the analyzer gas inlets be at or near ambient pressure usually managed by
placing a vent line on the incoming gas line (see Figure 3-18, Figure 3-19 and Figure
3-23).
By placing the pum
p down stream from the sample chamber, several problems are
avoided.
First, the pumping process heats and compresses the sample air complicating the
measurement process.
Additionally, certain physical parts of the pump itself are made of materials that
might chemically react with the sample gas.
Finally, in certain applications where the concentration of the target gas might be
high enough to be hazardous, maintaining a negative gas pressure relative to
ambient means that should a minor leak occur, no sample gas would be pumped
into the atmosphere surrounding analyzer.
Figure 13-3: T400 Pneumatic Diagram – Basic Unit
06870C DCN6332