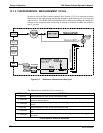
Theory of Operation T400 Ozone Analyzer Operator’s Manual
276
L is the absorption path, or the distance the light travels as it is being absorbed.
C is the concentration of the absorbing gas. In the case of the Model T400, Ozone
(O
3
).
is the absorption coefficient that tells how well O
3
absorbs light at the specific
wavelength of interest.
To solve this equation for C, the concentration of the absorbing Gas (in this case O
3
), the
application of a little algebra is required to rearrange the equation as follows:
Equation 13-2
Unfortunately, both ambient temperature and pressure influence the density of the
sample gas and therefore the number of ozone molecules present in the absorption tube
thus changing the amount of light absorbed.
In order to account for this effect the following addition is made to the equation:
Equation 13-3
Where:
T = sample temperature in Kelvin
P = sample pressure in inches of mercury
Finally, to convert the result into parts per billion (PPB), the following change is made:
Equation 13-4
In a nutshell the Model T400 Ozone Analyzer:
Measures each of the above variables: sample temperature; sample pressure; the
intensity of the UV light beam with
and without O
3
present,
Inserts known values for the length of the absorption path and the absorption
coefficient, and
Calculates the concentration of O
3
present in the sample gas.
06870C DCN6332