Chapter 5 Work in Edit mode 45
Work with channel strips in Edit mode
Channel strips overview
Channel strips are the building blocks of your patches. They contain the instruments and eects
for the sounds you use in performance. MainStage channel strips use the channel strip interface
common to many DAW and mixing applications. The main features of MainStage channel strips
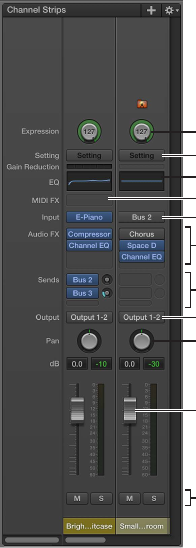
are shown below:
Expression control
Settings menu
Channel EQ
Input slot
Effect slots
Send slots and Send
Level knob
Output slot
Pan knob
Volume fader
Mute and Solo buttons
MIDI plug-in slot
•
Icon: Shows the type of channel strip for easy identication.
•
Expression control: Allows you to quickly adjust the expression value of the channel strip.
•
Settings menu: Allows you to load and save the entire routing conguration of a single channel
strip, including all loaded plug-ins and settings.
•
Channel EQ: Allows you to add an EQ eect to sculpt the sound of the channel strip signal
before applying other eects.
•
MIDI plug-in slots: Allow you to insert MIDI plug-ins into instrument channel strips.
•
Eect slots: Allow you to insert plug-ins into audio, instrument, aux, and output channel strips.
•
Send slots: Allow you to route a channel strip’s signal to an aux channel strip. Sends are
commonly used to apply the same eect or eects to several signals.
•
Send level knob: Controls the amount of signal sent to an aux channel strip. This knob appears
when a Send slot is activated.
•
Eect slot: Sets the channel strip’s input source. Depending on the channel strip type, it can
be a physical input, a bus, or a software instrument plug-in—in this case it is known as an
Instrument slot.
•
Output slot: Sets the channel strip’s output path. It can be a physical output or a bus.
•
Pan/Balance knob: On a mono channel strip, the Pan/Balance knob controls the position of the
signal in the stereo image. On a stereo channel strip, it controls the relative level of the left and
right signals at their outputs.