30-3
Catalyst 2960 and 2960-S Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-8603-09
Chapter 30 Configuring SNMP
Understanding SNMP
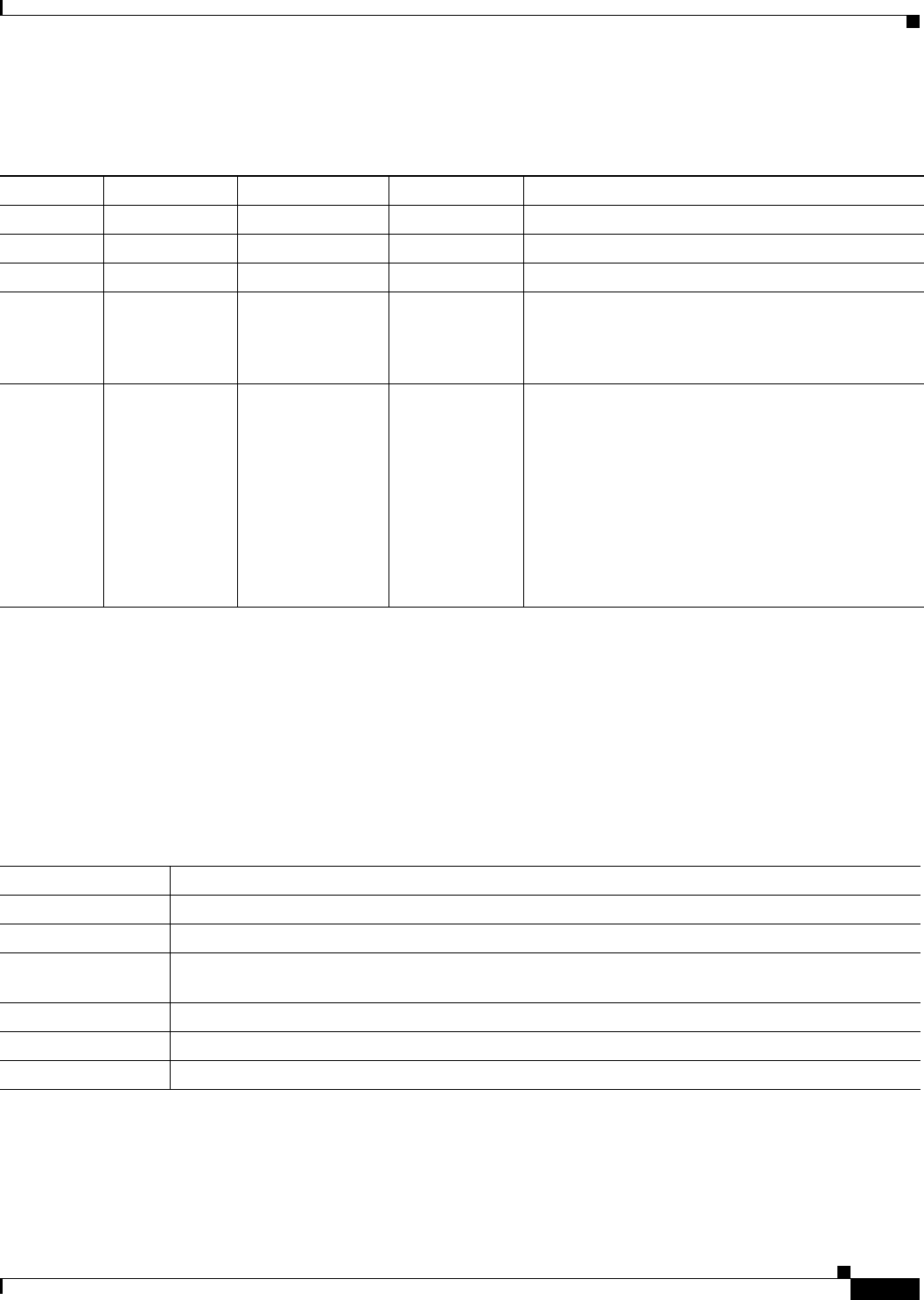
Table 30-1 identifies the characteristics of the different combinations of security models and levels.
You must configure the SNMP agent to use the SNMP version supported by the management station.
Because an agent can communicate with multiple managers, you can configure the software to support
communications using SNMPv1, SNMPv2C, or SNMPv3.
SNMP Manager Functions
The SNMP manager uses information in the MIB to perform the operations described in Table 30-2.
Table 30-1 SNMP Security Models and Levels
Model Level Authentication Encryption Result
SNMPv1 noAuthNoPriv Community string No Uses a community string match for authentication.
SNMPv2C noAuthNoPriv Community string No Uses a community string match for authentication.
SNMPv3 noAuthNoPriv Username No Uses a username match for authentication.
SNMPv3 authNoPriv Message Digest 5
(MD5) or Secure
Hash Algorithm
(SHA)
No Provides authentication based on the HMAC-MD5 or
HMAC-SHA algorithms.
SNMPv3 authPriv
(requires the
cryptographic
software image)
MD5 or SHA Data Encryption
Standard (DES)
or Advanced
Encryption
Standard (AES)
Provides authentication based on the HMAC-MD5 or
HMAC-SHA algorithms. Allows specifying the
User-based Security Model (USM) with these
encryption algorithms:
• DES 56-bit encryption in addition to
authentication based on the CBC-DES (DES-56)
standard.
• 3DES 168-bit encryption
• AES 128-bit, 192-bit, or 256-bit encryption
Table 30-2 SNMP Operations
Operation Description
get-request Retrieves a value from a specific variable.
get-next-request Retrieves a value from a variable within a table.
1
1. With this operation, an SNMP manager does not need to know the exact variable name. A sequential search is performed to find the needed variable from
within a table.
get-bulk-request
2
2. The get-bulk command only works with SNMPv2 or later.
Retrieves large blocks of data, such as multiple rows in a table, that would otherwise require the
transmission of many small blocks of data.
get-response Replies to a get-request, get-next-request, and set-request sent by an NMS.
set-request Stores a value in a specific variable.
trap An unsolicited message sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager when some event has occurred.


















