7-3
Catalyst 2960 and 2960-S Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-8603-09
Chapter 7 Managing Switch Stacks
Understanding Stacks
–
Stack Management Connectivity, page 7-14
–
Stack Configuration Scenarios, page 7-15
• This concept on stack topology changes:
–
Data Recovery After Stack Topology Changes, page 7-16
Stack Membership
Note A switch stack can have only Catalyst 2960-S stack members.
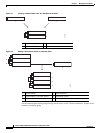
A standalone switch is a stack with one member that is also the master. You can connect one standalone
switch to another (Figure 7-1 on page 7-4) to create a stack containing two stack members, with one of
them as the master. You can connect standalone switches to an existing stack (Figure 7-2 on page 7-4)
to increase the stack membership.
If you replace a stack member with an identical model, the new switch functions with the same
configuration as the replaced switch (assuming that the new switch is using the same member number
as the replaced switch). For information about the benefits of provisioning a switch stack, see the “Stack
Offline Configuration” section on page 7-7. For information about replacing a failed switch, see the
“Troubleshooting” chapter in the hardware installation guide.
The operation of the stack continues uninterrupted during membership changes unless you remove the
master or you add powered-on standalone switches or stacks.
Note To prevent interrupted stack operations, make sure the switches that you add to or remove from the stack
are powered off.
After adding or removing members, make sure that the stack ring is operating at full bandwidth
(20 Gb/s). Press the Mode button on a member until the Stack mode LED is on. The last two port LEDs
on all switches in the stack should be green. If any one or both of any the last two port LEDs are not
green, the stack is not operating at full bandwidth.
• Adding powered-on switches (merging) causes the masters of the merging stacks to elect a master
from among themselves. The new master keeps its role and configuration and so do its members. All
remaining switches, including the former masters, reload and join the stack as members. They
change their member numbers to the lowest available numbers and use the configuration of the new
master.
• Removing powered-on members divides (partitions) the stack into two or more switch stacks, each
with the same configuration. This can create an IP address configuration conflict in your network.
If you want the stacks to remain separate, change the IP address or addresses of the newly created
stacks.