Replication can be used in various scenarios to achieve different levels of data protection.
Replication Scenarios Description
Fast backup and restore Maintain full copies of data for protection against data loss,
corruption, or user mistakes
Disaster recovery Mirror data to remote locations for failover during a disaster
Remote data access Applications can access mirrored data in read‐only or read‐write
mode if volumes are promoted or cloned
Online data migration Minimize downtime associated with data migration
Configuring replication is a three step process:
• Add a replication partnership between two FluidFS clusters.
• Add replication for a NAS volume.
• Run replication on demand or schedule replication.
How Replication Works
Replication leverages snapshots. The first time you replicate a NAS volume, the FluidFS cluster copies the
entire contents of the NAS volume. For subsequent replication operations, the FluidFS cluster copies only
the data that changed since the previous replication operation started. This allows for faster replication,
efficient use of system resources, and saves on storage space while keeping data consistent. Replication
is asynchronous, meaning that data is replicated to the target NAS volume based on a predefined
schedule, which can be different for each volume.
The amount of time replication takes depends on the amount of data on the NAS volume and the
amount of data that has changed since the previous replication operation.
Replication receives priority over serving data to clients.
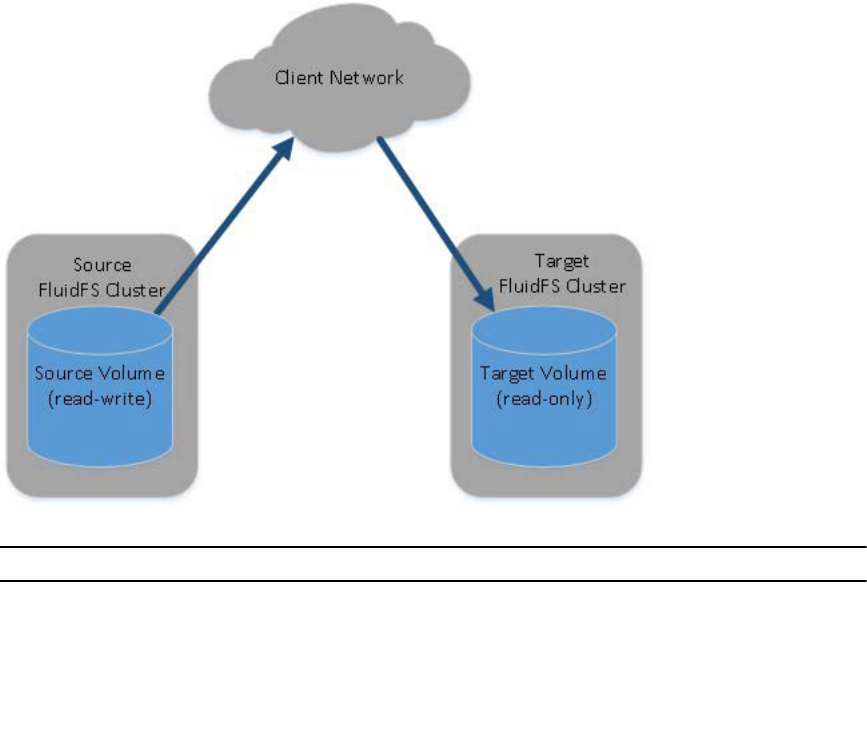
When replicating a NAS volume to another FluidFS cluster, the target FluidFS cluster must be set up as a
replication partner. Each FluidFS cluster may have multiple replication partners, enabling you to replicate
134


















