Section 21 IEBus
TM
Controller
R01UH0134EJ0400 Rev. 4.00 Page 1099 of 2108
Sep 24, 2014
SH7262 Group, SH7264 Group
(b) Unlocking
When the control bits indicate the lock (H'3, H'A, or H'B) or unlock (H'6) operation and the byte
data for the number of bytes specified by the message length bits are transmitted/received in a
single communications frame, the slave unit is unlocked by the master unit. In this case, the bit
(bit 2) relevant to locking in the byte indicating the slave status is cleared to 0.
Note that locking and unlocking are not done in broadcast communications.
Note: * There are three ways to cause a locked unit to unlock itself.
Perform a power-on reset
Put the unit in deep standby mode
Issue an unlock command through the IEBus command register (IECMR)
Note that the LCK flag in IEFLG can be used to check whether the unit is locked or
unlocked.
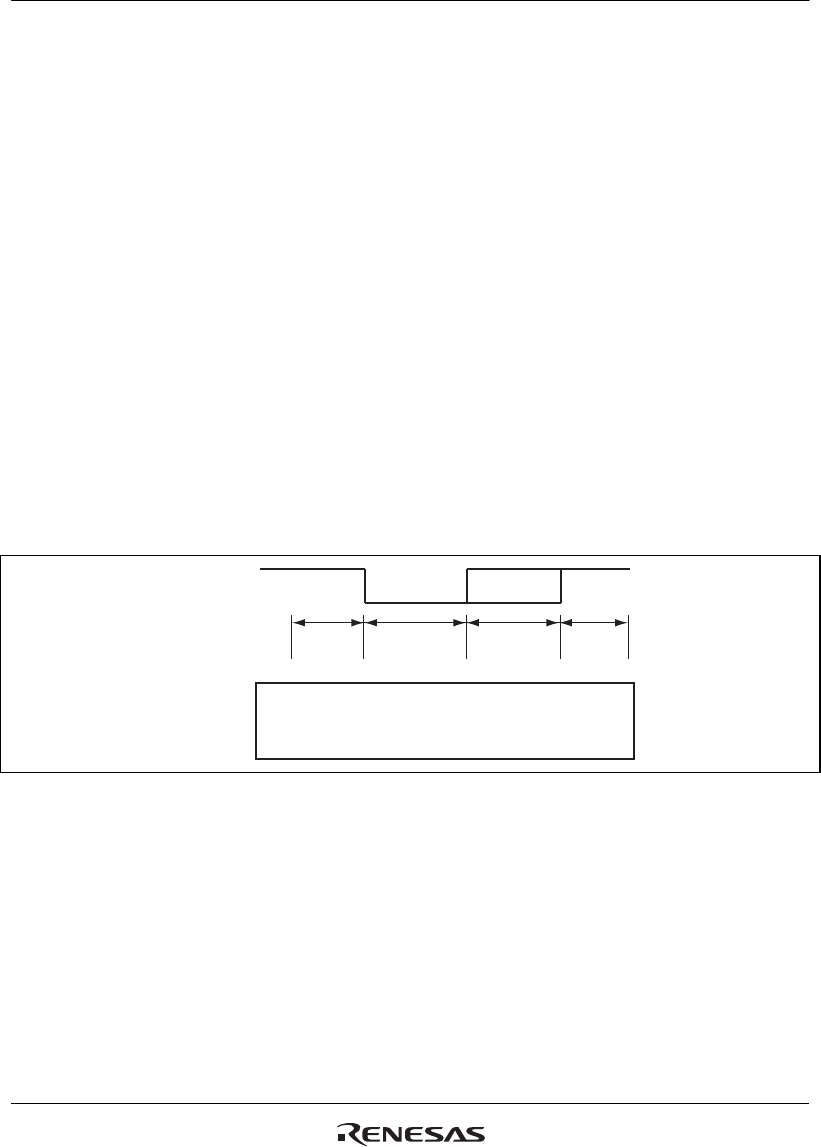
21.1.4 Bit Format
Figure 21.4 shows the bit format (conceptual diagram) configuring the IEBus communications
frame.
Logic 1
Logic 0
Active low: Logic 1 = low level and logic 0 = high level
Active high: Logic 1 = high level and logic 0 = low level
Preparation
period
Synchronous
period
Data
period
Halt
period
Figure 21.4 IEBus Bit Format (Conceptual Diagram)
Each period of the bit format for use of active high signals is described below.
Preparation period: first logic 1 period (high level)
Synchronous period: subsequent logic 0 period (low level)
Data period: period indicating bit value (logic 1: high level, logic 0: low level)
Halt period: last logic 1 period (high level)


















