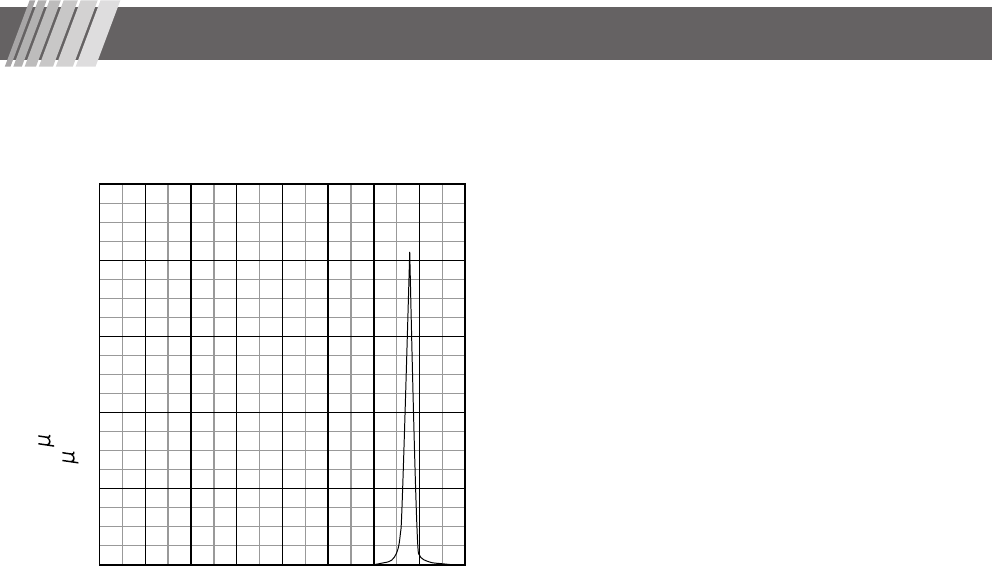
39
• The relative spectral output of the instrument
• The spectrally-weighted photochemical source radiance, both aphakic LB and aphakic LA
LB = 0.0352 mW/(cm
2
•
sr) 305nm to 700nm
LA = 0.0352 mW/(cm
2
•
sr) 305nm to 700nm
(informative)
Spectrally weighted photochemical radiances LB and LA give a measure of the potential that exists of a beam of
light to cause photochemical hazard to the retina. LB gives the measure for eyes in which the crystalline lens is in
place. LA gives this measure either for eyes in which the crystalline lens has been removed (aphakes) and has not
been replaced by a UV-blocking lens or for the eyes of very young children.
The value stated for this ophthalmic instrument gives a measure of hazard potential when the instrument is oper-
ated at maximum intensity and maximum aperture. Values of LB or LA over 80mW/(cm
2
•
sr) are considered high for
beams which wholly fill a dilated pupil.
The retinal exposure dose for a photochemical hazard is a product of the radiance and the exposure time. For
instance, at a radiance level of 80mW/(cm
2
•
sr), 3 min irradiation of the dilated (8mm diameter) pupil would cause
the retinal exposure dose level to attain the recommended exposure limit. If the value of radiance were reduced to
40mW/(cm
2
•
sr), twice that time (i.e.6min) would be needed to reach the recommended limit. The recommended
exposure dose is based on calculations arising from the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygien-
ists (ACGIH) - Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents (1995-1996 edition).
While no acute optical radiation hazards have been identified for ophthalmic instruments, it is recommended that
the intensity of light directed into the subject's eye be limited to the minimum level which is necessary for diagno-
sis.
Infants, aphakes and persons with diseased eyes will be at greater risk. The risk may also be increased if the
person being examined has had any exposure with the same instrument or any other ophthalmic instrument using
a visible light source during the previous 24 h. This will apply particularly if the eye has been exposed to retinal
photography.
(µW/(cm
2
• nm))
300 400 500 600 700
5
4
3
2
1
0
Wavelength (nm)
Energy( J) for image capturing light
Power( W) for illumination light
14. Photochemical Hazard (ISO 15004:1997)


















