2-54
Static Virtual LANs (VLANs)
Special VLAN Types
■ Monitoring Shared Resources: The Management VLAN feature shares
internal switch resources with several other features. The switch provides
ample resources for all features. However, if the internal resources
become fully subscribed, the Management VLAN feature cannot be con-
figured until the necessary resources are released from other uses. For
information on determining the current resource availability and usage,
refer to the appendix titled “Monitoring Resources” in the Management
and Configuration Guide for your switch.
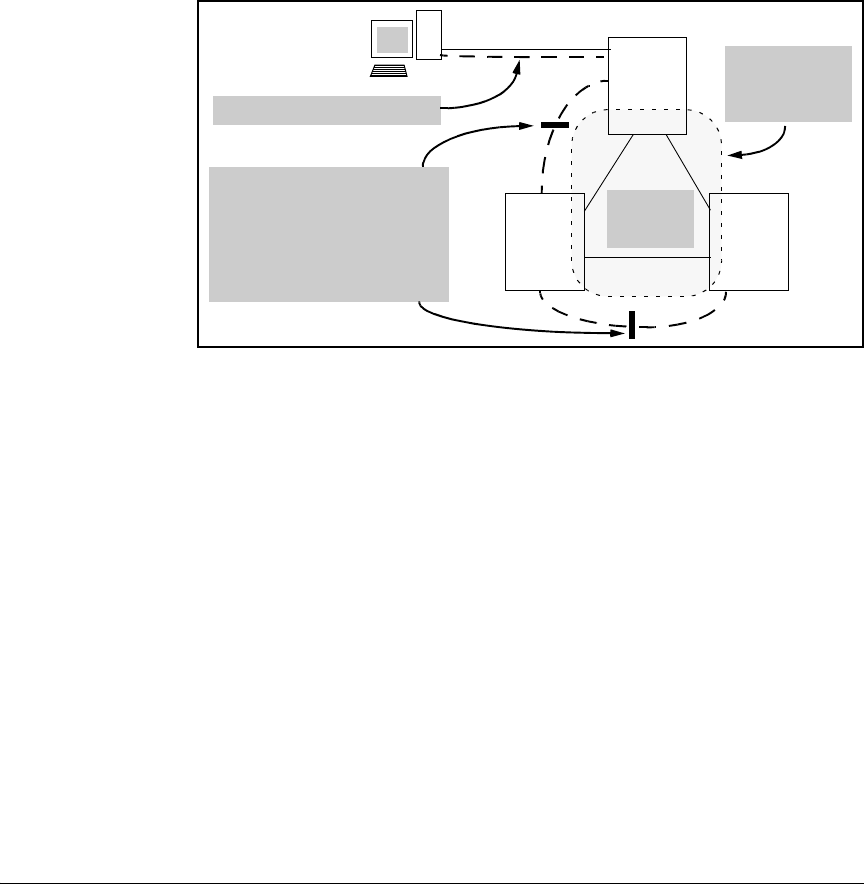
Figure 2-37. Example of Inadvertently Blocking a Management VLAN Link by
Implementing Spanning Tree
Voice VLANs
Configuring voice VLANs separates voice traffic from data traffic and shields
your voice traffic from broadcast storms. This section describes how to
configure the switch for voice VLAN operation.
Operating Rules for Voice VLANs
■ You must statically configure voice VLANs. GVRP and dynamic VLANs do
not support voice VLAN operation.
■ Configure all ports in a voice VLAN as tagged members of the VLAN. This
ensures retention of the QoS (Quality of Service) priority included in voice
VLAN traffic moving through your network.
■ If a telephone connected to a voice VLAN includes a data port used for
connecting other networked devices (such as PCs) to the network, then
you must configure the port as a tagged member of the voice VLAN and a
tagged or untagged member of the data VLAN you want the other net-
worked device to use.
VLAN 20 (Management VLAN)
VLAN 10
VLAN 30
VLAN 40
Mesh Domain
Includes
Membership in
Three VLANs
Switch
1
Switch
2
Switch
3
Even though the ports on the
Management VLAN link do not
belong to any of the VLANs in the
mesh, the link will be blocked if
you enable Spanning Tree. This is
because Spanning Tree operates
per-switch and not per-VLAN.


















