2-19
Static Virtual LANs (VLANs)
Multiple VLAN Considerations
Example of an Unsupported Configuration and How To
Correct It
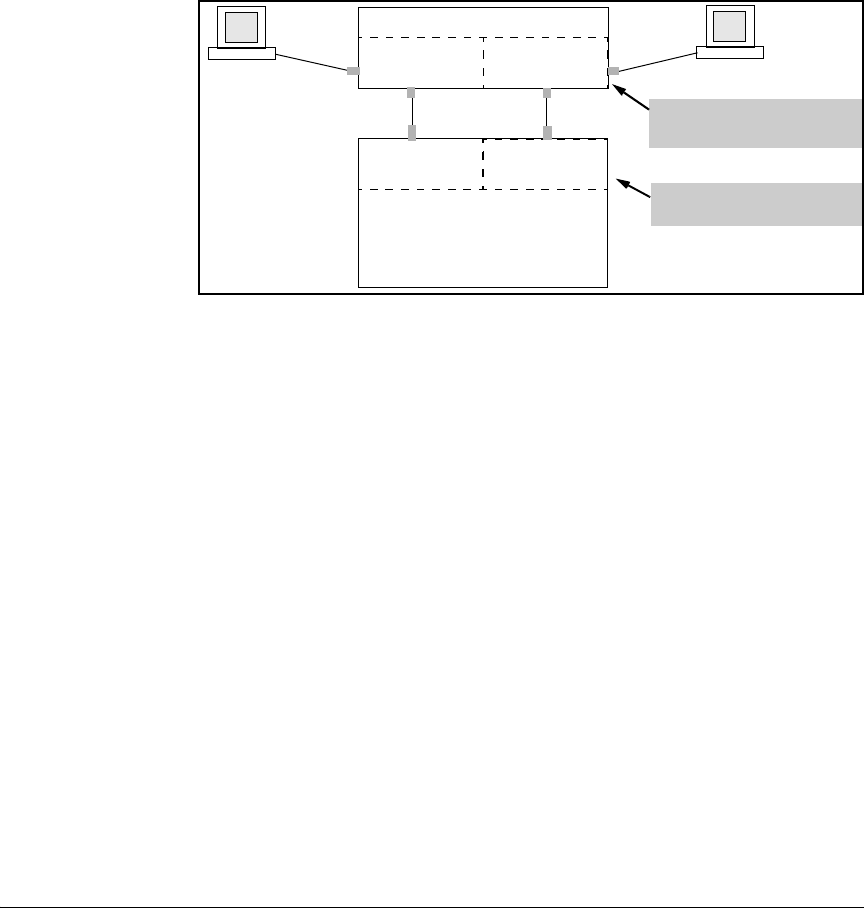
The Problem. In figure 2-9, the MAC address table for Switch 6600 will
sometimes record the switch as accessed on port A1 (VLAN 1), and other times
as accessed on port B1 (VLAN 2):
Figure 2-9. Example of Invalid Configuration for Single-Forwarding to Multiple-
Forwarding Database Devices in a Multiple VLAN Environment
In figure 2-9, PC “A” sends an IP packet to PC “B”.
1. The packet enters VLAN 1 in the Switch 6600 with the 6120 switch’s MAC
address in the destination field. Because the 6600 has not yet learned this
MAC address, it does not find the address in its address table, and floods
the packet out all ports, including the VLAN 1 link (port “A1”) to the 6120
switch. The 6120 switch then routes the packet through the VLAN 2 link
to the 6600, which forwards the packet on to PC “B”. Because the 6600
received the packet from the 6120 switch on VLAN 2 (port “B1”), the 6600’s
single forwarding database records the 6120 switch as being on port “B1”
(VLAN 2).
2. PC “A” now sends a second packet to PC “B”. The packet again enters
VLAN 1 in the Switch 6600 with the 6120 switch’s MAC address in the
destination field. However, this time the Switch 6600’s single forwarding
database indicates that the 6120 is on port B1 (VLAN 2), and the 6600 drops
the packet instead of forwarding it.
3. Later, the 6120 switch transmits a packet to the 6600 through the VLAN 1
link, and the 6600 updates its address table to indicate that the 6120 switch
is on port A1 (VLAN 1) instead of port B1 (VLAN 2). Thus, the 6600’s
information on the location of the 6120 switch changes over time. For this
Switch
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
6120 Switch
(Same MAC address for all
VLANs.)
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
This switch has multiple
forwarding databases.
This switch has a single
forwarding database.
PC “A”
PC “B”
A1
B1
C1
D1


















