2-20
Static Virtual LANs (VLANs)
Multiple VLAN Considerations
reason, the 6600 discards some packets directed through it for the 6120
switch, resulting in poor performance and the appearance of an intermit-
tent or broken link.
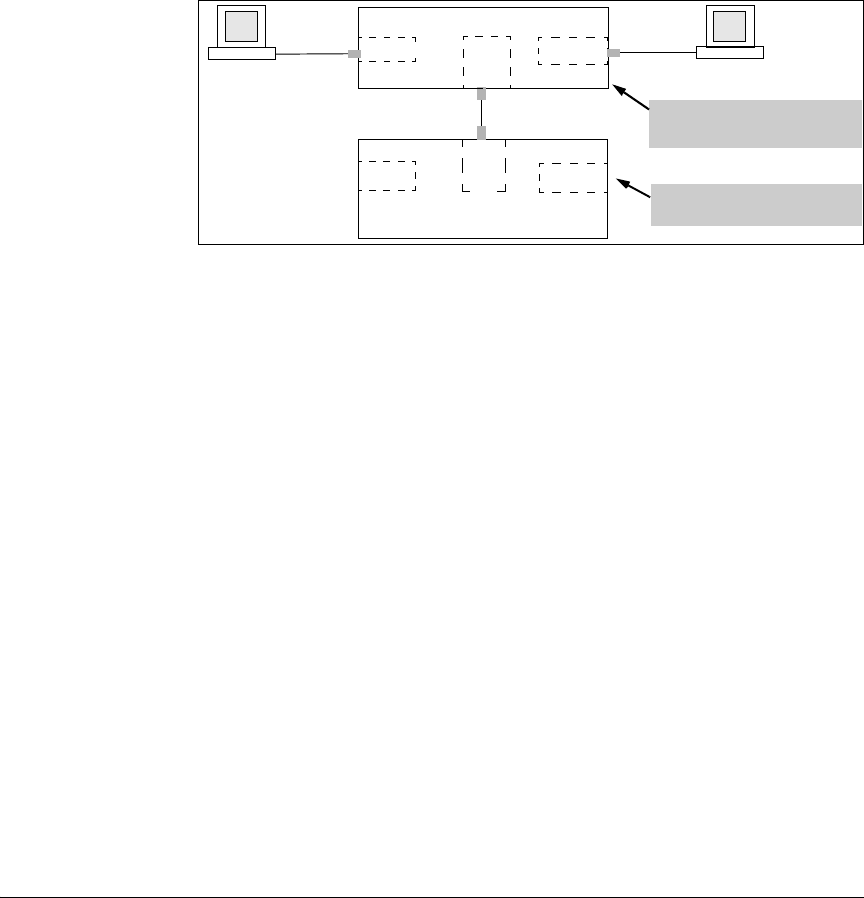
The Solution. To avoid the preceding problem, use only one cable or port
trunk between the single-forwarding and multiple-forwarding database
devices, and configure the link with multiple, tagged VLANs.
Figure 2-10. Example of a Solution for Single-Forwarding to Multiple-Forwarding
Database Devices in a Multiple VLAN Environment
Now, the 6600 forwarding database always lists the 6120 MAC address on port
A1, and the 6600 will send traffic to either VLAN on the 6120.
To increase the network bandwidth of the connection between the devices,
you can use a trunk of multiple physical links rather than a single physical link.
Multiple Forwarding Database Operation
If you want to connect one of the switches covered by this guide to another
switch that has a multiple forwarding database, you can use either or both of
the following connection options:
■ A separate port or port trunk interface for each VLAN. This results in a
forwarding database having multiple instances of the same MAC address
with different VLAN IDs and port numbers. (See table 2-4.) The fact that
the switches covered by this guide use the same MAC address on all VLAN
interfaces causes no problems.
■ The same port or port trunk interface for multiple (tagged) VLANs. This
results in a forwarding database having multiple instances of the same
MAC address with different VLAN IDs, but the same port number.
Allowing multiple entries of the same MAC address on different VLANs
enables topologies such as the following:
Switch
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
6120 Switch
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
This switch has multiple
forwarding databases.
This switch has a single
forwarding database.
PC “A”
PC “B”
VLAN
1 & 2
VLAN
1 & 2
A1
C1


















