2-21
Static Virtual LANs (VLANs)
Configuring VLANs
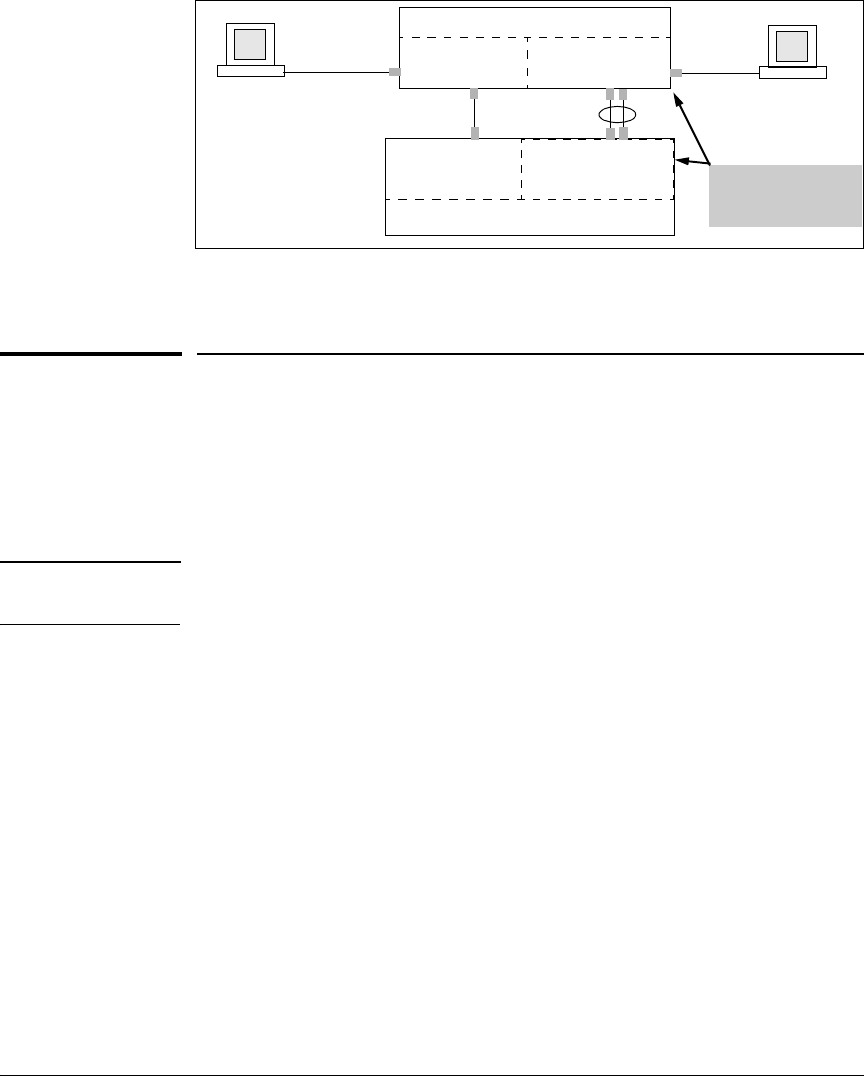
Figure 2-11. Example of a Valid Topology for Devices Having Multiple Forwarding
Databases in a Multiple VLAN Environment
Configuring VLANs
Menu: Configuring Port-Based VLAN Parameters
The Menu interface enables you to configure and view port-based VLANs.
Note The Menu interface configures and displays only port-based VLANs. The CLI
configures and displays port-based and protocol-based VLANs (page 2-27).
In the factory default state, support is enabled for up to 256 VLANs. (You can
reconfigure the switch to support up to 256 (vids up to 4094) VLANs.) Also, in
the default configuration, all ports on the switch belong to the default VLAN
and are in the same broadcast/multicast domain. (The default VLAN is also
the default Primary VLAN—refer to “The Primary VLAN” on page 2-45.) In
addition to the default VLAN, you can configure additional static VLANs by
adding new VLAN names and VIDs, and then assigning one or more ports to
each VLAN. (The maximum of 256 VLANs includes the default VLAN, all
additional static VLANs you configure, and any dynamic VLANs the switch
creates if you enable GVRP—page 3-1.) Note that each port can be assigned
to multiple VLANs by using VLAN tagging. (See “802.1Q VLAN Tagging” on
page 2-40.)
Switch
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
6120 Switch
VLAN 1
VLAN 2
Both switches have
multiple forwarding
databases.


















