KEY
COOCEPTS
Continuing
the
notion
of
the
logical
I/O
processor,
the
Attached
Processor
fetches
instructions,
provides
the
instructions
needed
to
alter
the
flow
of
execution,
and
performs
arithmetic,
logic
and
data
transfer
operations
within
the
Peripheral
Subsystem.
INTERFACE
P~SSOR
The
IP
completes
the
logical
I/O
processor
by
providing
data
paths
between
the
Peripheral
Subsystem and
the
432
system.
The
IP
also
provides
functions
which
effectively
extend
the
AP's
instruction
set
so
that
software
running
on
the
logical
I/O
processor
can
operate
in
the
432
system.
Since
these
facilities
are
software-controlled,
they
are
discussed
in
the
next
section.
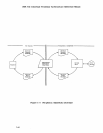
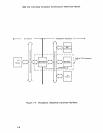
As
figure
1-4
shows,
the
Interface
Processor
presents
both
a
Peripheral
Subsystem bus
interface
and a
standard
432
processor
packet
bus
interface.
By
br
idging
the
two
buses,
the
IP
provides
the
hardware
link
that
permits
data
to
flOll between
the
432
system
and
the
Peripheral
Subsystem.
The
Interface
Processor
connects
to
the
432
system
in
exactly
the
same way
as
a
GDP.
Thus,
in
addition
to
being
able
to
access
432
memory,
the
IP
supports
other
432
hardware-based
facilities,
including
interprocessor
comnunication,
alarm
signaling
and
functional
redundancy
checking.
On
the
I/O
subsystem
side,
the
IP
provides
a
very
general
bus
interface
that
can
be
adapted
to
any
standard
8-
or
16-bit
microprocessor
bus,
including
Intel's
Multibus'lM
architecture,
as
well
as
the
component
buses
of
the
MCS-8S
and
iAPX
86
families.
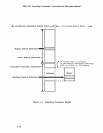
The
IP
is
oonnected
to
the
Peripheral
Subsystem
bus
as
if
it
were a
memory
component;
it
occupies
a
blOCK
of
memory
addresses
up
to
64k
bytes
long.
Like
a menory,
the
IP
behaves
passively
within
the
Peripheral
Subsystem
(except
as
noted
below).
It
is
driven
by
Peripheral
Subsystem
memory
references
that
fall
within
its
address
range.
The
IP
generally
responds
like
a
memory
canponent.
The
Interface
Processor
also
supplies
an
interrupt
signal.
The
Interface
Processor
uses
this
line
to
notify
its
Attached
Processor
that
an
event
has
occurred
which
requires
fts
attention.
Interrupt
handling
software
on
the
AP
may
read
status
information
provided
by
the
IP
to
identify
the
nature
of
the
event.
1-9