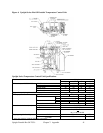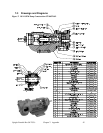
Upright Portable Hot Oil TCUs Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 36
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
6-1 Introduction
The utmost in safety precautions should be observed at all times when working on or around
the machine and the electrical components. All normal trouble-shooting must be
accomplished with the power off, line fuses removed, and with the machine tagged as out of
service.
The use of good quality test equipment cannot be over-emphasized when troubleshooting is
indicated. Use a good ammeter that can measure at least twice the AC and DC current that
can be encountered for the machine. Be sure that the voltmeter has at least minimum
impedance of 5,000 OHMS-per-volt on AC and 20,000 OHMS-per-volt on DC scales.
Popular combination meters, VOM and VTVM can be selected to provide the necessary
functions.
Before making haphazard substitutions and repairs when defective electrical components are
malfunctioning, we recommend that you check the associated circuitry and assemblies for
other defective devices. It is common to replace the obviously damaged component without
actually locating the real cause of the trouble. Such hasty substitutions will only destroy the
new component. Refer to wiring diagrams and schematics.
Locating mechanical problems, should they occur, is relatively straightforward. When
necessary, refer to the parts catalog section.
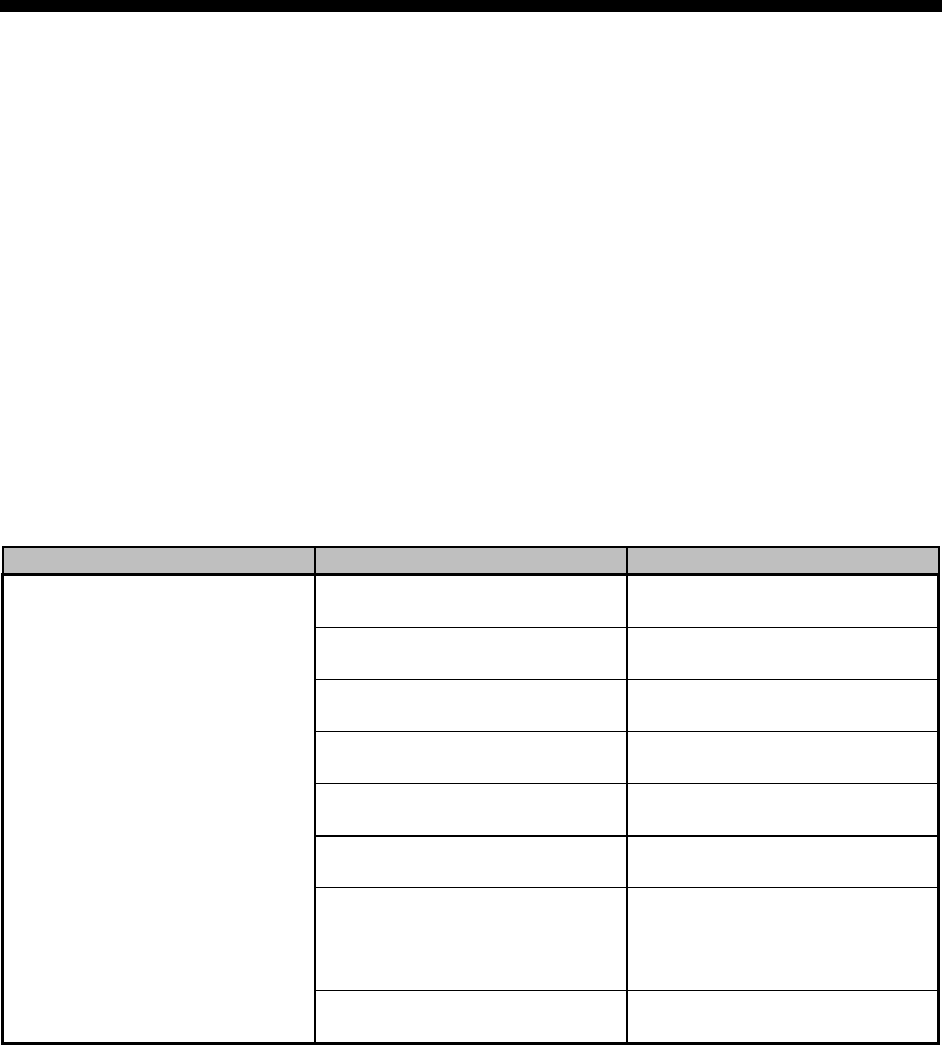
Problem Possible cause Corrective action
Undersized connectors/lines.
Increase size of connectors/
water lines.
Long connecting lines between
unit and mold.
Move the unit closer to the mold
and shorten connecting lines.
Serpentine flow through mold.
Connect lines for parallel flow
instead of series flow.
Blocked line in mold.
Check mold for metal chips or
deposits. Clean mold.
Quick disconnect fitting with
check valve.
Remove and replace fitting or
valve.
Carbon build-up in unit piping
or fittings.
Clean or replace affected piping.
Replace fluid.
Faulty TCU.
Check unit by opening the
manual bypass to determine if
the TCU contols the set point
temperature.
Temperature fluctuations/rapid
cycling from hot to cold.
Reversed probes.
Switch Return and Delivery
probes.