1-7
Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points
OL-30644-01
Chapter 1 Overview of Access Point Features
Network Configuration Examples
Bridges
Access points can be configured as root or non-root bridges. In this role, an access point establishes a
wireless link with a non-root bridge. Traffic is passed over the link to the wired LAN. Access points in
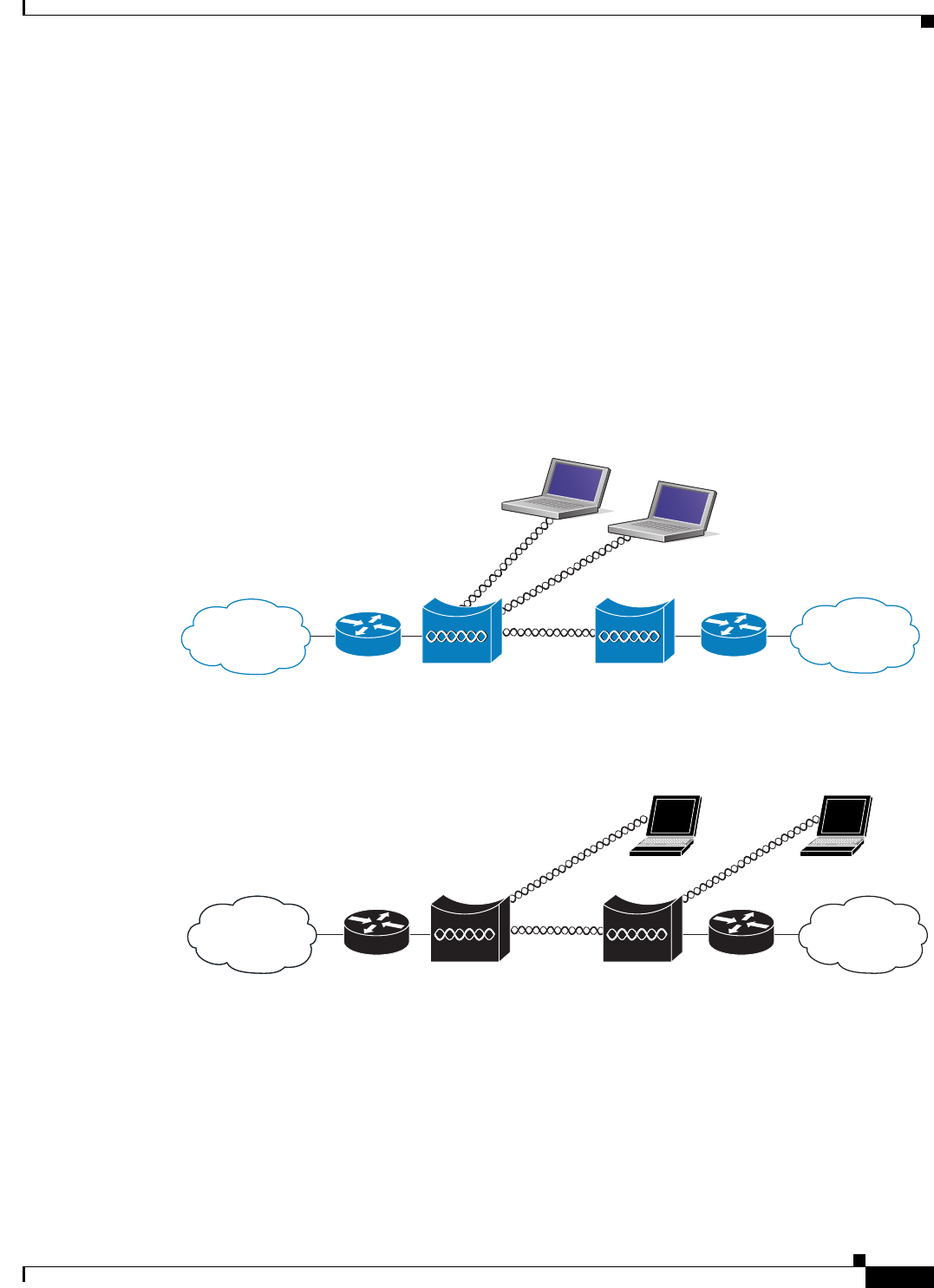
root and non-root bridge roles can be configured to accept associations from clients. Figure 1-3 shows
an access point configured as a root bridge with clients. Figure 1-4 shows two access points configured
as a root and non-root bridge, both accepting client associations. Consult the “Configuring the Role in
Radio Network” section on page 6-3 for instructions on setting up an access point as a bridge.
When wireless bridges are used in a point-to-multipoint configuration the throughput is reduced
depending on the number of non-root bridges that associate with the root bridge. With a link data rate at
54 Mbps, the maximum throughput is about 25 Mbps in a point-to-point link. The addition of three
bridges to form a point-to-multipoint network reduces the throughput to about 12.5 Mbps.
Figure 1-3 Access Point as a Root Bridge with Clients
Figure 1-4 Access Points as Root and Non-root Bridges with Clients
Workgroup Bridge
You can configure access points as workgroup bridges. In workgroup bridge mode, the unit associates
to another access point as a client and provides a network connection for the devices connected to its
Ethernet port. For example, if you need to provide wireless connectivity for a group of network printers,
Root bridge Non-root bridge
135447
Root bridge Non-root bridge
135446
