Onboard Diagnostics
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)
14 Craftsman 14063
Generic DTCs are codes that are used by all vehicle manu-
facturers. The standards for generic DTCs, as well as their
definitions, are set by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
Manufacturer-Specific DTCs are codes that are controlled by
the vehicle manufacturers. The Federal Government does not
require vehicle manufacturers to go beyond the standardized
generic DTCs in order to comply with the new OBD2 emissions
standards. However, manufacturers are free to expand beyond
the standardized codes to make their systems easier to
diagnose.
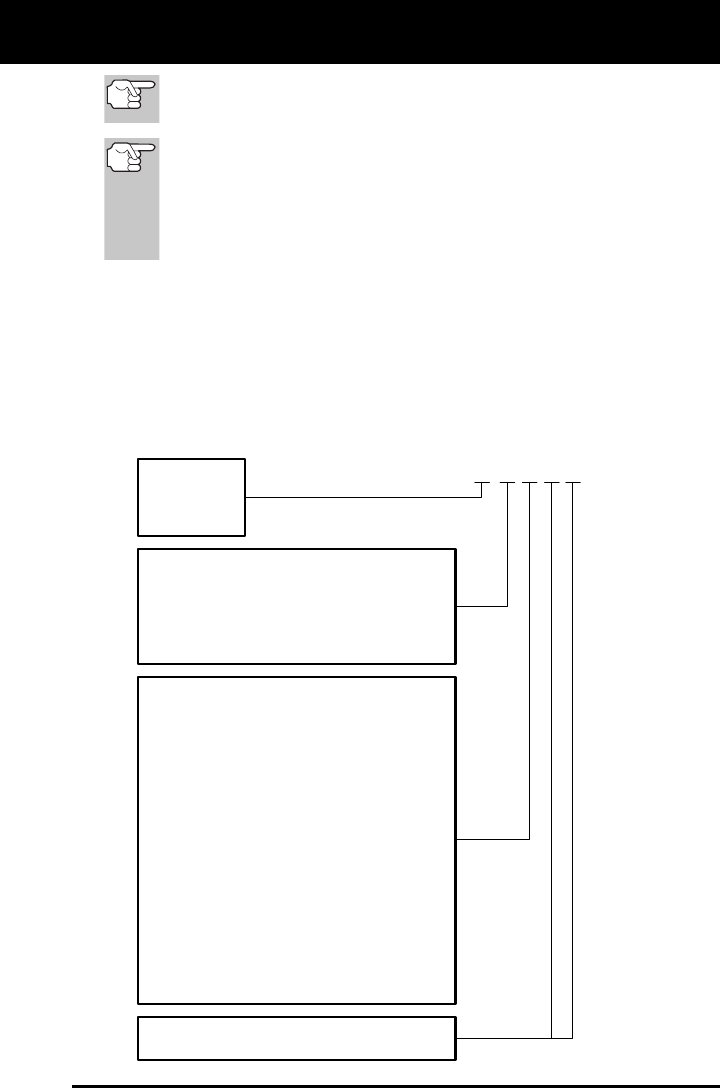
The 3rd character is a letter or a numeric digit (0 thru 9, A thru F).
It identifies the specific system or sub-system where the problem is
located.
The 4th and 5th characters are letters or numeric digits (0 thru 9, A
thru F). They identify the section of the system that is malfunctioning.
P 0 2 0 1
B
C
P
U
-
-
-
-
Body
Chassis
Powertrain
Network
-
-
-
-
Generic
Manufacturer Specific
Generic ("P" Codes) and Manufacturer
Specific ("B", "C" and "U" Codes)
Includes both Generic and Manufacturer
Specific Codes
0
1
2
3
Identifies what section of the system
is malfunctioning
Identifies the system where the problem is
located. "P" Code systems are listed below.
"B", "C" and "U" Code systems will vary.
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
C
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Fuel and Air Metering; Auxiliary Emission
1 - Fuel and Air Metering
Controls
Fuel and Air Metering (injector circuit
malfunction only)
Ignition System or Misfire
Auxiliary Emission Control System
Vehicle Speed Control and Idle Control
System
Computer Output Circuits
Transmission
8 - Transmission
9 - Transmission
A - Hybrid Propulsion
B - Hybrid Propulsion
Hybrid Propulsion
OBD2 DTC EXAMPLE
P0201 - Injector Circuit Malfunction, Cylinder 1


















